

Table of Contents
CONTENTS
- CEMENT
- COMPOSITION OF ORDINARY CEMENT
- HYDRATION OF CEMENT
- TYPES OF CEMENT
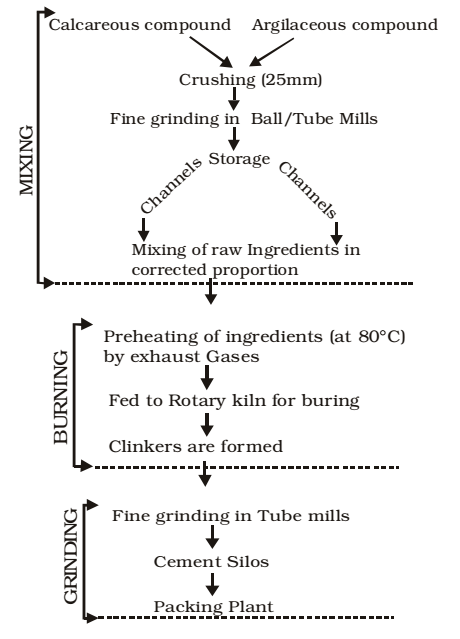
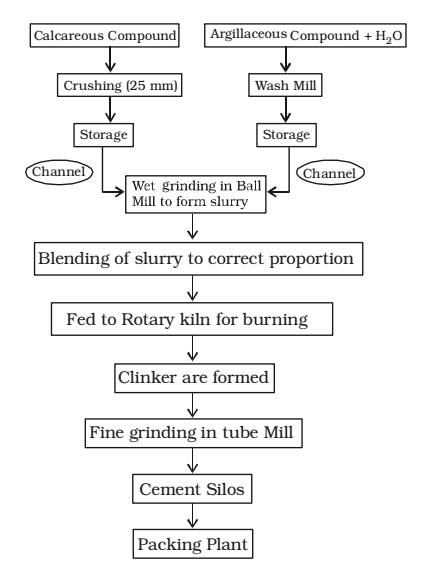
- MANUFACTURING OF CEMENT
- CHARACTERISTICS AND PROPERTIES OF CEMENT
- CONCRETE
- PROPERTIES OF CONCRETE
- PREPARATION OF CONCRETE
- MORTAR
- ADMIXTURES
- TYPES OF CONCRETE

CEMENT
The history of cementing material is as old as the history of engineering construction. The natural cement is obtained by burning and crushing the stones containing clay, carbonate of lime and some amount of carbonate of magnesia. The natural cement is brown in colour and its best variety is known as the Roman cement.
CEMENT AND LIME
The point of difference between ordinary cement and lime are the following
- Lime is white in colour whereas colour of cement is greyish.
- Portland/lime blends are manufactured in a blending facility using portland cement and hydrated type ‘S’ lime, whereas masonry cements are manufactured in a cement plant using portland clinker, plasticizers, and air entraining agent together.
- Cement paste sets quickly than lime.
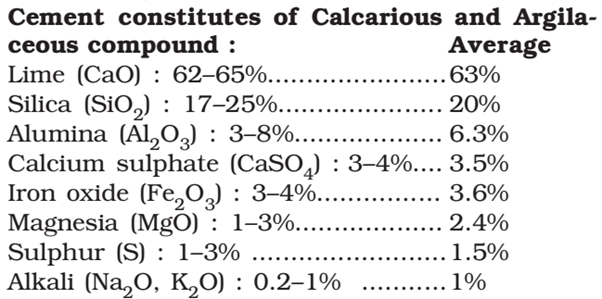
COMPOSITION OF ORDINARY CEMENT
The raw material required for manufacture of portland cement are calcareous materials such as limestone or chalk and argillaceous material such as clay or shale. In calcareous materials, the calcium carbonate predominates and in argillaceous materials, it is clay which predominates.
IES MASTER CIVIL ENGINEERING GATE STUDY MATERIALS : CLICK HERE
FUNCTION OF DIFFERENT CONSTITUENTS OF CEMENT:
- Lime (62–65%): It imparts strength and soundness, when it makes cement (volume change) unsound causing it to expand and disintegrate. If it is in deficiency, it reduces strength of cement and causes it to set quickly.
- Silica (17-25%): It also imparts strength to the cement. If in excess, it increases the strength of the cement but also increases setting time of cement. Cement not set quickly (if batching plant and site are far away).
- Alumina (3-8%): It imparts quick setting property to cement. It acts as a flux and reduces the clinkering temperature during the burning of cement. If in excess, it weakens the cement.
- CaSO4 (3-4%): It is generally added in the form of gypsum (CaSO4. 2H2O) in cement. It is used to increase the initial setting time of cement. (Cement start to lose its plasticity with final setting time plasticity is lost completely).
- Iron Oxide (3–4%): It imparts strength, hardness and colour to cement (It induces reddish brown tint to the cement).
- Magnesia (1-3%): It also imparts strength and colour. If in excess, it makes the cement unsound. (It induces yellowish tint to cements).
- Sulphur (1-3%): It is also responsible for imparting soundness to cement. [Soundness due to lime and Magnesia can be measured easily. but no test is available to test soundness and effect of adding sulphur].
- Alkali (0.2 –1%): Alkali present in cement causes efflorescence and staining of structure in which it is used for construction. These alkalies react with H2O resulting in the development of white grey spots over the surface of structure leading to its staining. The raw materials used for the manufacture of cement consists mainly of lime, silica, alumina and iron oxide These oxides interact with one another in the kiln at high temperature to form more complex compound. The relative proportions of these oxide compositions are responsible for influencing the various properties of cement in addition to rate of cooling and fineness of grinding.
CONCRETE
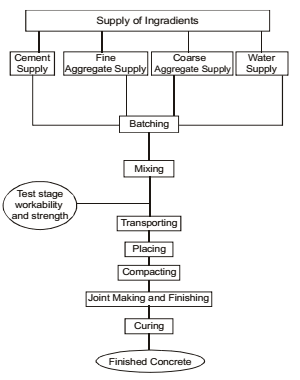
Concrete is the most widely man-made construction material. It is a mixture of cement, water, sand and gravel or crushed aggregates. The mixture when placed in forms and allowed to cure becomes hard like stone. Concrete is also known as an artificial stone as it possesses many similar characteristics of a natural stone. The process of making concrete is called concreting. In order to obtain finished concrete, the process in sequence is known as concrete chain. Each concreting operation (process) should be carefully done and controlled to obtain the desired strength and durability of concrete.
ACE CIVIL ENGINEERING GATE STUDY MATERIALS : CLICK HERE
Properties of concrete in Plastic stage
- Good workability: Workability in simple term can be defined as “the ease with which the concrete can be mixed, transported, placed and compacted. A workable concrete mix does not result in bleeding or segregation.
- Freedom from Segregation: Segregation means separation of coarse aggregates from concrete in its Plastic Stage.
- Freedom from bleeding: The appearance of water along with some particles of cement and very fine sand on the surface of freshly placed concrete is known as bleeding. The term ‘water gain’ also means the same.
- Prevention from harshness: The concrete mix that does not give smooth surface with a certain amount of trowelling is known as harsh mix.
Properties of concrete in Hardness Stage.
In hardness stage, the properties of concrete are:
(a) Strength
The ability of concrete to resist load is called strength. Stronger concretes are stiffer, impermeable and durable. The strength of concrete may be:
- Crushing Strength
- Tensile Strength
- Bond Strength
- Shear Strength
Lime is white in colour whereas colour of cement is greyish.
(b) Durability
Durability of concrete is the resistance to deterioration and disintegration due to temperature change variations in moisture content, action of water containing chemicals and weathering.
(c) Impermeability
Impermeability is the resistance of the concrete to the flow of water into the pre-space in it. Impermeability of concrete should be high.
(d) Dimensional changes
The following are the properties involving dimensional changes.
- Shrinkage: Shrinkage in concrete should be minimum.
- Elasticity: A good concrete should have adequate elasticity or plasticity.
- Thermal expansion: A good concrete should have minimum thermal expansion.
- Creep: Creep concrete is sometimes beneficial and sometimes disadvantageous.
MADE EASY CIVIL ENGINEERING GATE STUDY MATERIALS : CLICK HERE
Advantages of Concrete
As compared to other construction materials, concrete has the following advantages.
- Green or freshly prepared concrete can easily be moulded in any desired shape.
- The materials used in the manufacture of concrete are easily available.
- It is more durable, free from corrosion and weathering if properly designed.
- It is not liable to rot or decay.
- It is fire resistant.
- It is almost impermeable to moisture.
- It provides good architectural appearance to the structure.
- The concrete can be pumped and hence can be used in difficult positions.
- It is economical in the long run because of low maintenance cost of structures made from it.
- Concrete can even be sprayed on and filled into fine cracks or voids for repairs by gruting process.
- The concrete become stronger with age.
- Construction of all types of structure is possible by reinforcing the concrete with steel. Even earthquake resistant structures can be constructed.
Uses of concrete in comparison to other building materials
The uses of concrete in comparison to other building materials are:
- It is used for the construction of structure, especially for foundation in wet location.
- It is used for providing damp-proof course. For this purpose, rich mix of plain cement concrete is generally used.
- It is used for the construction of structural members subjected to bending or shear stresses. For this purpose, reinforced or prestressed concrete is used.
- It is used for the construction of bridges, water tank industrial buildings etc.
- It is used for the construction of concrete pipes, poles, sleepers, piles, etc. For this purpose, prestressed concrete is used.
- It is used for the construction of thin shells, shelled roots (dome shaped), swimming pool etc.
- It is used for the construction of fire proofing and insulation applications. For this purpose, light weight concrete is commonly used.
CONCRETE TECHNOLOGY STUDY MATERIAL FOR RRB JE PDF CIVILENGGFORALL
DOWNLOAD LINK : CLICK HERE
PASSWORD : CivilEnggForAll
OTHER USEFUL BOOKS
- BUILDING MATERIALS – MOCK TEST 1 (QUICK)
- TELANGANA STATE PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION – ASSISTANT ENGINEER 2023 – TSPSC AE 2023 CIVIL ENGINEERING EXAM SOLVED PAPER WITH EXPLANATIONS PDF FREE DOWNLOAD
- SSC JE 2023 CIVIL ENGINEERING (CPWD/CWC/MES) EXAM SOLVED PAPER PDF FREE DOWNLOAD
- BIHAR PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION ASSISTANT ENGINEER (BPSC AE) 2022 CIVIL ENGINEERING EXAM SOLVED PAPER WITH EXPLANATIONS PDF
- NHPC (NATIONAL HYDROELECTIC POWER CORPORATION) JUNIOR ENGINEER NHPC JE 2022 CIVIL ENGINEERING EXAM SOLVED PAPER PDF FREE DOWNLOAD

Leave a Reply