
CONTENTS
- GEOLOGICAL CYCLE
- PROPERTIES OF SOILS
- INDEX PROPERTIES OF SOILS
- SIEVE ANALYSIS
- STOKE’S LAW
- PREPARATION OF SOIL SUSPENSION
- SHRINKAGE ANALYSIS
- SENSITIYIVTY
- THIXOTROPY
- CLASSIFICATION OF SOILS
- COARSE GRAINED SOILS
- SOIL EXPLORATION
- EARTH PRESSURE
- RANKINE’S EARTH PRESSURE THEORY
- STRESSES IN SOIL
- PERMEABILITY
- SHEAR STRENGTH OF SOIL
- TESTS ON SOILS
- COMPACTION OF SOIL
- FACTORS AFFECTING COMPACTION
- SEEPAGE ANALYSIS
- COMPRESSIBILITY OF SOIL
- CONSOLIDATION OF SOIL
- CONSOLIDATION TESTS
- DEGREE OF CONSOLIDATION
- TIME FACTOR
- SETTLEMENT ANALYSIS

GEOLOGICAL CYCLE
The process of formation of soil is termed as pedogenesis. Soil is generally formed due to the erosion of rocks which may be carried out either physically or chemically. The geological cycle of soil formation consists of four steps.

Physical agencies involved in erosion of rocks are flowing water, wind & ice. e.g. Gravel and sand. Chemical Agencies involved in the erosion are oxidation, carbonation & reduction. e.g. Silts and clays. If the eroded soil material remains over the parent rock, it is termed as residual soil & if the eroded soil material is transported (by any of the above mentioned agencies), the soil is termed as transported soil. Due to physical weathering of the rocks, mineral constituent of the soil does not differ from the parent rock & due to chemical weathering mineral, constituent differs from the parent rock.
Types of Soils according to the Transporting Agency Transported Soils
- ALLUVIAL SOIL: It is the type of soil that is deposited from suspension in flowing water. It is a physical agency. generally found along the banks of the rivers. It is normally deposited at the bed of the river.
- LACUSTRINE SOIL (Physical Agency): It is the type of soil, that is deposited from suspension in still & fresh water of the lakes.
- MARINE SOIL (Physical Agency): It is the type of soil formed from suspension in marine water, It is formed at the bed of sea.
- AEOLINE SOIL (Physical Agency): It is the type of soil transported by wind.
- GLACIAL SOIL: Here (Physical weathering is not that prominent as flow is not continuous so, graded. It is the type of soil which is transported by ice.
SOIL MECHANICS IES MASTER GATE STUDY MATERIAL : CLICK HERE
Some Special/Typical Soil
- LOESS SOIL: It is uniformly graded silt that is transported by wind & is slightly cemented due to the presence of calcium carbonate & clay mineral like Montmorelonite. It is found in deserts. and is uniformly (Poorly) graded soil.
- MARL SOIL (Organic soil): It is finely graded silty cemented soil of marine origin. It is generally formed due to the decomposition of dead cell & bones of aquatic life (fishes & plants).
- BENTONITE SOIL: It is formed due to chemical weathering of volcanic ash which is generally used as a lubricant in drilling.
- LATERITE SOIL: This type of soil is formed due to the leaching of washing out of silicons Matter from parent rock (i.e. Silica will not be present in this soil). It is found in hilly areas, (Western Ghats, Eastern Ghats etc.) having humid condition.
- COLLOVIAL SOIL (Tallus): It is also known as Tallus soil. It is formed due to transportation by gravitational force in hilly areas generally in the valleys.
- GUMBO SOIL: It is sticky, highly plastic dark coloured soil.
- PEAT SOIL: It is highly organic almost consisting entirely of vegetative matters in different stages of decomposition. Its colour varies from black to dark brown & possess organic odour. It is highly fibrous & compressive in nature.
- MUCK SOIL: It is the mixture of fine particulated inorganic soil and dark brown or black decomposed organic matter. It is generally formed, where indeficient sewerage facilities are found or due to the over flooding of the river.
GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING ACE GATE NOTES : CLICK HERE
Common soils in which Engineering Problems
- Marine deposits: Marine deposits are very soft and may contain organic matter. These possess low shear strength and high compressibility hence, posses problems as foundation material.
- Black Cotton soils: These soils have been formed from basalt or trap and contain clay mineral montmorillonite, which is responsible for the excessive swelling and shrinkage characteristics of the soil.
- Desert soils: These are wind blown deposits of sand. Dune sand is non-plastic uniformly graded fine sand. Problems associated with these soils are of soil stablization for roads and runways, reducing settlement under static and dynamic loads and reducing its perviousness to make it suitable for storage and transportation.
SHEAR STRENGTH OF SOIL
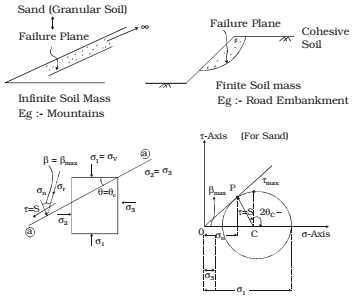
Shear strength of a soil is resistance offered by a soil against shear deformation. It is equal to shear stress developed on critical plane or failure plane. Critical plane is that plane at which angle of resultant stress with the normal of that plane is maximum.
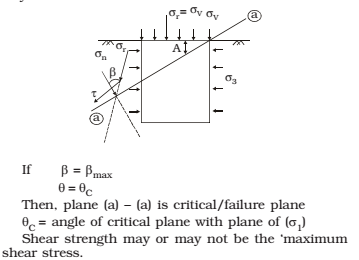
Factors determining shear strength of soil
- Interlocking between molecules
- frictional resistance [Rolling and sliding friction]
- Attraction between molecules [cohesion & adhesion].
GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING ACE GATE STUDY MATERIAL : CLICK HERE
Stress
Stress is an internal force acting per unit area of a surface. It is a vector quantity. It has normally, two components one, that acts normal to the sectional plane, and other that acts along the plane. The Normal Component which acts along the plane is called tangential stress or shearing stress. Note: Granular soils [Sands and Gravel] derive their strength from interlocking and friction whereas fine cohesive soils [clays] derive their strength from cohesion and adhesion, however medium grain soil [silt] derive their strength both from friction & cohesion. The shear failure plane in granular soil [Sand] is usually linear whereas in cohesive soil is curved [arc of circle]. In case of infinite soil mass failure plane is found linear but in case of finite soil mass, failure plane is found curved.
TYPE OF SHEAR STRENGTH TEST
Type of test on the basis of drainage condition: The choice of test depends upon the type of soil & the purpose of test for which it is required. It also depends upon drainage facilities available at the fields.
- Unconsolidated–Undrained test [U–U test]: It is a quick test which takes 5 to 7 minutes. In this test, neither flow of water from the soil is permitted during cell pressure stage all round pressure and nor during back pressure stage (only 1 direction (vertical) loading). The stage is called deviator stage. Such a shear strength will be called undrained shear strength. This test is suitable for saturated clays having low permeability subjected to fast rate of loading.
- Consolidated-Undrained test [C-U test]: In this test drainage is permitted in 1st stage [cell pressure stage], whereas during back pressure stage/ shear stage the drainage is not permitted. It means the 2nd stage is undrained. This test is usually used for, the investigation of stability of earthern test, against the failure which may occur due to sudden drawdown. It is also called consolidated Quick Test.
- Consolidated-drained test [C-D test]: It is most time taken, because drainage is permitted during cell pressure stage and back pressure stage both. 4-6 weeks are required to complete the test. So, it is also called “Slow test”. In this test considerable volume change is recorded due to expulsion of pore water. This test is suitable for saturated sands for investigation of stability under long term condition.
GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIAL FOR RRB JE PDF CIVILENGGFORALL
DOWNLOAD LINK : CLICK HERE
PASSWORD : CivilEnggForAll
OTHER USEFUL BOOKS
- RAJASTHAN STAFF SELECTION BOARD (RSSB) JUNIOR ENGINEER DIPLOMA CIVIL ENGINEERING EXAM 2022 – HINDI & ENGLISH MEDIUM SOLVED PAPER – FREE DOWNLOAD PDF (CivilEnggForAll.com)
- ISRO TECHNICAL ASSISTANT EXAM 2022 – CIVIL ENGINEERING – HINDI & ENGLISH MEDIUM – SOLVED PAPER – FREE DOWNLOAD PDF (CivilEnggForAll.com)
- MADHYA PRADESH PUBLIC SERVICE (MPPSC) COMMISSION – ASSISTANT ENGINEER EXAM – MPPSC AE 2021 CIVIL ENGINEERING – SOLVED PAPER WITH EXPLANATIONS – PDF FREE DOWNLOAD
- BIHAR PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION (BPSC) ASSISTANT ENGINEER EXAM – 2022 – CIVIL ENGINEERING – SOLVED PAPER – FREE DOWNLOAD PDF (CivilEnggForAll.com)
- ODISHA PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION – OPSC AEE PANCHAYATI RAJ EXAM 2021 – SOLVED PAPER WITH EXPLANATION – FREE DOWNLOAD PDF





















