
CONTENTS
- Stones
- Sources of Stones
- Bricks
- Clamps
- Lime
- Mortar
- Timber
- Cast Iron
- Steel
- Bituminous Materials
- Paints, Varnishes and Distempers

Qualities of Good Bricks:
- The bricks should be table-moulded, well-burnt in kilns, copper-coloured, free from cracks and with sharp and square edges. The colour should be uniform and bright.
- The bricks should give a clear metallic ringing sound when struck with each other.
- The bricks when broken should show a bright homogeneous and uniform compact structure free from voids.
- The bricks should not absorb water more than 20% by wt. for first class bricks and 22% by wt. for second class bricks, when soaked in cold water for a period of 24 hours.
- The bricks should be sufficiently hard. No impression should be left on brick surface, when it is scratched with finger nail.
- The brick should not break into pieces when dropped flat on hard ground from a height of about one metre.
- The bricks should have low thermal conductivity and they should be sound proof.
- The bricks, when soaked in water for 24 hours, should not show deposits of white salts when allowed to dry in shade.
- No brick should have crushing strength below 55 kg/cm2.
IES MASTER CIVIL GATE STUDY MATERIALS : CLICK HERE
Size and Weight of Bricks
The bricks which are not standardized are known as the traditional bricks. For India, a brick of standard size 19 cm x 9 cm x 9 cm is recommended by the BIS. With mortar thickness the size of such a brick becomes 20 cm x 10 cm x 10 cm and it is known as the nominal size of the modular brick. Thus, the nominal size of brick includes the mortar thickness. The average weight of a brick will be about 3 to 3.5 kg. Brick tiles should be 19 cm x 9 cm x 4 cm in size.

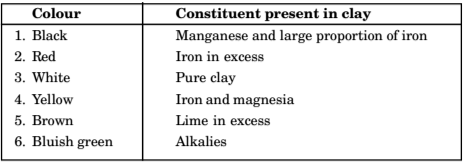
Classification of Binding Materials:
- Air Binding Material: Strength gained only in the presence of air e.g. Gypsum, acid-resistant cement, quick lime etc.
- Hydraulic Binding Material: Strength gained air and also in water e.g. Portland cement, hydraulic lime, etc. Such binding material can be used for constructions above ground, below ground and under water.
- Autoclave Binding Material: e.g. Lime-silica, sand, Portland cements.
Classification of Limes
The limes which are obtained by calcination of limestones are broadly classified into the following three categories:
- Fat lime, high calcium lime, pure lime, rich lime or white lime.
- Hydraulic lime or water lime
- Floor lime, impure lime or lean lime. It sets or hardens rely slowly.

Uses of Lime
- It is used as chemical raw material in the purification of water and for sewage treatment.
- It is used as a flux in the metallurgical industry.
- It is used as a matrix for concrete and mortar.
- It is used in the production of glass.
- It is used for making mortar for masonry work.
- It is used for plastering of walls and ceilings.
- It is used for the soil stabilization and for improving soil for agricultural purposes
- It is used for white washing and for serving as a base coat for distemper.
ACE CIVIL ENGINEERING GATE STUDY MATERIALS : CLICK HERE
Properties of the Fat Lime
- It hardens very slowly.
- It sets slowly in presence of air.
- It slakes vigorously.
- Its colour is perfectly white.
- It has a high degree of plasticity.
- It is soluble in water which is changed frequently.
Properties of Cement
- It gives strength to masonary.
- It is an excellent binding material.
- It is easily workable.
- It offers good resistance to moisture.
- It possesses good plasticity.
- It stiffens or hardens early.
MADE EASY CIVIL ENGINEERING GATE NOTES : CLICK HERE
Functions of Cement Ingredients
- Lime: The lime in excess makes cement unsound and causes the cement to expand and disintegrate. On the other hand, if lime is in deficiency, the strength of cement is decreased and it causes cement to set quickly.
- Silica : It imparts strength to the cement due to the formation of dicalcium and tricalcium silicates. If Silica is present in excess quantity, the strength of cement increases but at the same time, its setting time is prolonged.
- Alumina: It imparts quick selting property to the cement. The Alumina should not be present in excess amount as it weakens the cement.
- Calcium Sulphite: It is the gypsum and its function is to increase the initial setting time of cement.
- Iron Oxide: It imparts colour, hardness and strength to the cement.
- Magnesia: It imparts hardness and colour to the cement. A high content of magnesia makes the cement unsound. Sulphur: A very small amount of sulphur is useful in making sound cement. If it is in excess, it causes cement to become unsound.
- Alkalies: If they are in excess, they cause a number of troubles such as alkali aggregate reaction, efflorescence and staining.
BUILDING MATERIALS STUDY MATERIAL FOR SSC JE PDF CIVILENGGFORALL
DOWNLOAD LINK : CLICK HERE
PASSWORD : CivilEnggForAll
OTHER USEFUL BOOKS
- RAJASTHAN STAFF SELECTION BOARD (RSSB) JUNIOR ENGINEER DIPLOMA CIVIL ENGINEERING EXAM 2022 – HINDI & ENGLISH MEDIUM SOLVED PAPER – FREE DOWNLOAD PDF (CivilEnggForAll.com)
- ISRO TECHNICAL ASSISTANT EXAM 2022 – CIVIL ENGINEERING – HINDI & ENGLISH MEDIUM – SOLVED PAPER – FREE DOWNLOAD PDF (CivilEnggForAll.com)
- MADHYA PRADESH PUBLIC SERVICE (MPPSC) COMMISSION – ASSISTANT ENGINEER EXAM – MPPSC AE 2021 CIVIL ENGINEERING – SOLVED PAPER WITH EXPLANATIONS – PDF FREE DOWNLOAD
- BIHAR PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION (BPSC) ASSISTANT ENGINEER EXAM – 2022 – CIVIL ENGINEERING – SOLVED PAPER – FREE DOWNLOAD PDF (CivilEnggForAll.com)
- ODISHA PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION – OPSC AEE PANCHAYATI RAJ EXAM 2021 – SOLVED PAPER WITH EXPLANATION – FREE DOWNLOAD PDF





















