
TOPICS COVERED
- Alphabet & Number Arrangement
- Analogy & Classification
- Series/Coding – Decoding
- Directions
- Time Sequence
- Number and Ranking test
- Blood Relations
- Problem Solving
- Logical Venn Diagram
- Syllogisms
- Arithmetic Reasoning
- Clock and Calendar
- Statement and Conclusion
- Non verbal Reasoning
- Spatial Ability

Note : This material consists of the topic wise problem types, required theory and explanation to solve the problems, exercises, hints and solutions for solving the exercises. Even though this book covers most of the topics required for the examination, still we recommend you to cover as many models as possible which are out of this book’s coverage.
Analogy and Classification – Types of questions
- Tool & object based analogy: This establishes a relationship between a tool and the object in which it works. Similar relations has to be discovered from answer choices.
- Synonym based analogy: In such type of analogy two words have similar meaning.
- Causes & effect based analogy: In such type of analogy 1 st word acts and the 2nd word is the effect of that action.
- Opposite relationship (Antonym) based analogy: In such type of analogy the two words of the question pair are opposite in meaning. Similar relations has to be discovered from the answer choice word pairs.
- Classification based analogy: This type of analogy is based on biological, physical, chemical or any other classification. In such problems the 1st word may be classified by the 2nd word and vice-versa.
- Finished product & raw material based analogy: In such type of analogy the 1st word is the raw material and 2nd word is the end product of that raw material and vice-versa.
- Symbolic relationship based analogy: In such type of analogy, the 1st word is the symbol of the 2nd word and vice-versa.
- Analogy based on letters (or meaningless words)
Case I: (Forward alphabetical sequence) Examples: CD: FG:: PQ: UV Here CD and FG are in the natural alphabetical sequence. Similarly, PQ & UV are in the natural alphabetical sequence.
Case II: (Backward or opposite alphabetical sequence) Example: DC: GF:: QP: VU In fact this case is opposite of case I
Case III: (Vowel – consonant relation) Example ATL: EVX:: IPR: ORS Here, the 1st two words start with the 1st two vowels A & E and the next two words start with the next two vowels I & O. Last two letter of every word are consonants.
Case IV: Example (Skip letter relation) ABC: FGH:: IJK: NOP Here between ABC & FGH two letters skip and they are D & E. Similarly, between IJK & NOP two letters skip and they are L & M. Case V: (Jumbled letters relation) Example: LAIN: NAIL:: EVOL: Love Here the 1st term gets reversed to produce the 2nd term and similar relation is shown in between 3rd and 4th term.
IES MASTER CIVIL GATE STUDY MATERIALS : CLICK HERE
Types of Classification
- Letter/meaningless word based classification
- Meaningful word based classification
- Digit based classification
- General knowledge based classification
1. Letter/meaningless word based classification – Such classifications are based on letters of English alphabet. So many groups of letters are given in the question in which one group is different from remaining groups and hence the different group will be our answer.
2. Meaningful words based classification – In such type of classification we have to take odd word out of the given group of meaningful words.
3. Digit based classification – In such type of classifications digits or numbers are given to find out one number that is not a part of the group of remaining numbers.
4. General knowledge based classification – Such classification is done on the basis of our general knowledge. No doubts that this is a word based classification but without having general knowledge this type of questions can not be solved.
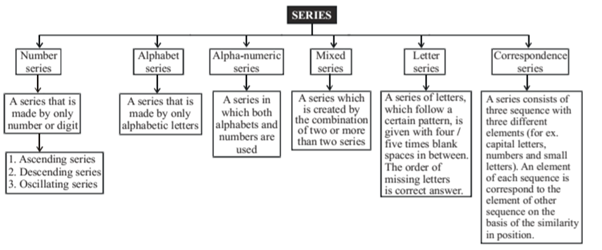
SERIES/CODING AND DECODING TYPES
In number series, relationship between the terms is of any kind. For example.
- Consecutive even numbers
- Consecutive odd numbers
- Consecutive prime numbers
- Square of numbers
- Cubes of numbers
- Square root of numbers
- Omission of certain number of letter in any consecutive order
- Addition /subtraction/ multiplication/ division by some number (For Ex. A.P & G.P) or any other relation.
TYPE I (CODING BY LETTER SHIFTING)
Pattern 1: Coding in forward sequence
Pattern 2: Coding in backward sequence.
Pattern 3: Coding based on skipped sequence.
TYPE II (CODING IN FICTIONS LANGUAGE)
In some cases of coding-decoding, fictions language is used to code some words. In such questions, the codes for a group of words is given. In such types of problems, codes for each word can be found by eliminating the common words.
TYPE III (CODING BASED ON NUMBERS)
Pattern 1: When numerical values are given to words.
Pattern 2: When alphabetical code value are given for numbers.
TYPE IV (MATHEMATICAL OPERATIONS WITH THE POSITION NUMBERS OF LETTERS)
Sample Example: In a certain code, if ‘TALE’ is written as 38, then how will you code ‘CAME’ using the same coding scheme?
Explanation: Look at the numbered alphabet and write down the number corresponding to the letters of the word ‘TALE’.
T | A | L | E = 20 | 1 | 12 | 5
The fact that the code for ‘TALE’ is 38, gives you a clue that the code is probably obtained by performing an arithmatical operations of the numbers of each other. Let us see: 20 + 1 + 12 + 5 = 38 Thus, the code for ‘CAME’ is C A M E 3 + 1 + 13 + 5 = 22, hence code for ‘CAME’ = 22
CIVIL ENGINEERING ACE GATE STUDY MATERIALS : CLICK HERE
DIRECTIONS ON MAP
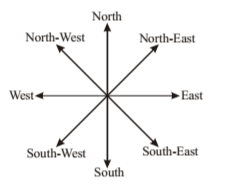
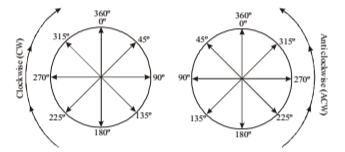
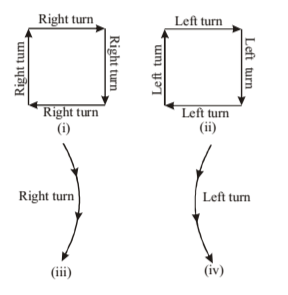
Important points regarding direction
- If our face is towards North, then after left than our face will be it towards West while after right turn it will be towards East.
- If our face is towards South, then after left turn our face will be towards East and after right turn it will be towards West.
- If our face is towards East, then after left turn our face will be forwards North and after right turn it will be towards South.
- If our face is towards West, then after left turn our face will be towards South and after right turn it will be towards North.
- If our face is towards North-West, then after left turn our face will be towards South-West and after right turn it will be towards North-East.
- If our face is towards South-West, then after left turn our face will be towards South-East and after right turn it will be towards North-West.
- If our face is towards South-East, then after left turn our face will be towards North-East and after right turn it will be towards South-West.
- If our face is towards North-East, then after left turn our face will be towards North-East and after right-turn it will be towards South-East.
TIME SEQUENCE
To solve problems related to time sequence, let us gather 1st the following information:
- Minute = 60 seconds
- Hour = 60 minutes
- Day = 24 hours
- Week = 7 days
- Month = 4 weeks
- Year = 12 months
- Ordinary year = 365 days
- Leap year = 366 days
- Century = 100 years
RANKING TEST
In these types of questions, generally the ranks of a person both from the top and from the bottom are mentioned and the total number of persons is asked.
- Formula 1: Total number of persons in a row or class = (Rank of a person from upper end or left end) + (Rank of that person from lower on right end) – 1
- Formula 2: Rank of a person from lower or right end = (Total number of persons in row) – (Rank of that person from upper or left end) + 1.
- Formula 3: Rank of a person from upper or left end = (Total number of persons in a row) – (Rank of that person from lower or right end) + 1
BLOOD RELATION TYPE OF PROBLEMS
- General problems of blood relation
- Blood relation based on family tree
- Coded blood relationship.
A. Without the information of gender, no relationship can be established between two people. For example, If given that R is the child of P & Q, then we can only say that P & Q are the parents of R. But we can not find out:
(i) R is the son of P & Q or R is the daughter of P & Q.
(ii) Who is mother of R and who is father of R.
But if we have given that P is a male, Q is a female and R is male, then we can easily say that R is the son of P and Q. Further we can also say that P is father of R and Q is mother of R.
B. Gender can not be decided on the basis of name. For example in Sikh community the names like Manjit, Sukhvinder etc. are the names of both male and female. Similarly, in the Hindu Community ‘Suman’ is the name of both male and female.
Remember – Solution Tips
- While solving blood relation based question, first of all find out that two persons between whom a relationship has to be established.
- Next, try to find out middle relation
- Finally find out the relationship between two persons to be identified for this purpose.
ABOVE THEORY IS THE BRIEF SAMPLE OF VARIOUS TOPICS EXPLANATION TAKEN FROM THIS BOOK
RRB JE GENERAL INTELLIGENCE AND REASONING GUIDE BY CIVILENGGFORALL PDF
DOWNLOAD LINK : CLICK HERE
PASSWORD : CivilEnggForAll
ACE ACADEMY GATE GENERAL ABILITY NOTES : CLICK HERE
OTHER USEFUL BOOKS
- RAJASTHAN STAFF SELECTION BOARD (RSSB) JUNIOR ENGINEER DIPLOMA CIVIL ENGINEERING EXAM 2022 – HINDI & ENGLISH MEDIUM SOLVED PAPER – FREE DOWNLOAD PDF (CivilEnggForAll.com)
- ISRO TECHNICAL ASSISTANT EXAM 2022 – CIVIL ENGINEERING – HINDI & ENGLISH MEDIUM – SOLVED PAPER – FREE DOWNLOAD PDF (CivilEnggForAll.com)
- MADHYA PRADESH PUBLIC SERVICE (MPPSC) COMMISSION – ASSISTANT ENGINEER EXAM – MPPSC AE 2021 CIVIL ENGINEERING – SOLVED PAPER WITH EXPLANATIONS – PDF FREE DOWNLOAD
- BIHAR PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION (BPSC) ASSISTANT ENGINEER EXAM – 2022 – CIVIL ENGINEERING – SOLVED PAPER – FREE DOWNLOAD PDF (CivilEnggForAll.com)
- ODISHA PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION – OPSC AEE PANCHAYATI RAJ EXAM 2021 – SOLVED PAPER WITH EXPLANATION – FREE DOWNLOAD PDF





















