
CONTENTS
- TYPES OF SECTION
- TYPES OF STRUCTURAL STEELS
- CONNECTIONS
- FAILURE OF JOINTS
- PERMISSIBLE STRESSES
- ARRANGEMENT OF RIVETS
- ECCENTRIC CONNECTIONS
- WELDED CONNECTIONS
- TENSION MEMBERS
- COMPRESSION MEMBERS
- EFFECTIVE LENGTH
- ANGLE STRUTS
- DESIGN OF COMPRESSION MEMBERS
- LACINGS
- BATTENS
- COLUMN BASES
- GUSSETED BASE
- GRILLAGE FOUNDATION
- SLAB BASE
- BEAMS
- DESIGN FOR BENDING
- GANTRY GIRDERS
- BUILT UP BEAMS
- BEAM COLUMN
- PLATE GIRDERS
- WEB STIFFENERS
- PERMISSIBLE BENDING STRESSES
- CURTAILMENT OF FLANGE PLATES
- WEB STIFFENERS
- INDUSTRIAL ROOFS
- PURLINS AND GRITS
- ROOF TRUSS

TYPE OF SECTIONS
Rolled Steel Sections Steel structures are built with hot-rolled steel sections. The Indian Standards Institution has evolved a rational, efficient and economical series of Indian Standards (IS: 808-1964 and its parts, part I—1973, part II—1978. part III— 1979. part V—1976, and part VI—1976) for rolled steel beams, channels and angle sections to save steel in construction works. The following sections are standardized by the Indian Standards Institution.

STEEL STRUCTURES IES MASTER GATE STUDY MATERIAL : CLICK HERE
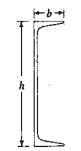
I-Sections
- Indian Standard Junior Beams (ISJB).
- Indian Standard Light Beams (ISLB).
- Indian Standard Medium Weight Beams (MB).
- Indian Standard Wide Flange Beams (ISWB).
- Indian Standard Column Section (SC) All above I-sections are designated along with the depth the respective section in mm, e.g. MB 200 is a hot-rolled steel, medium-weight beam of depth 200 mm.
Channel-sections
- Indian Standard Gate Channel (ISPG).
- Indian Standard Junior Channel (ISJC).
- Indian Standard Light Channel (ISLC).
- Indian Standard Medium Weight Channel with sloping flange (MC).
- Indian Standard Medium Weight Channel with parallel flange (MCP). All the above hot-rolled channel sections are designated along with the depth of the respective section, e.g. MC 200 is a medium weight channel of depth 200 mm.
STEEL STRUCTURES ACE GATE STUDY MATERIAL : CLICK HERE
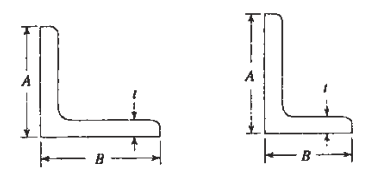
Angle-sections
- Indian Standard Equal Angles.
- Indian Standard Unequal Angles. Angle-sections are designated by abbreviation ISA along with the lengths of both legs and their thickness, e.g., ISA 6565, 8 mm or ISA 65 x 65 x 8 mm is an equal-angle section 8 mm thick and with both legs 65 mm long. The supplementary angle sections are designated by the size of “legs and their thickness without the prefix ISA.
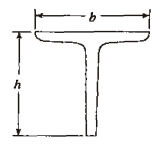
Tee-sections
- Indian Standard Rolled Normal Tee Bars (ISNT).
- Indian Standard Rolled Deep Legged Tee Bars (ISDT).
- Indian Standard Slit Light Weight Tee Bars (ISLT).
- Indian Standard Slit Medium Weight Tee Bars (ISMT).
- Indian Standard Slit Tee Bars from H-sections* (ISHT). Tee-sections are designated by the respective abbreviations followed by their depth, e.g. a normal tee-bar of depth 100 mm is designated by ISNT 100.
STEEL STRUCTURES MADE EASY GATE STUDY MATERIAL : CLICK HERE
BOLTED JOINTS
Bolts may be used in place of rivets for structure not subjected to vibrations. The following types of bolts are used in structures:
(i) Black bolts:
- Hexagonal black bolts are commonly used in steel works.
- They are made from low or medium carbon steels
- They are designated as black bolts M × d × l Where, d = diameter, and l = length of the bolts.
(ii) Precision and Semi Precision Bolts:
- They are also known as close tolerance bolts.
- Sometimes to prevent excessive slip, close tolerance bolts are provided in holes of 0.15 to 0.2 mm oversize. This may cause difficulty in alignment and delay in the progress of work.
- Types of Riveted and Bolted Joints
There are two types of riveted or bolted joints.
(i) Lap joint:
- The lap joint is that in which the plates to be connected overlap each other.
- The lap joint may have single-row, staggered or chain riveting.
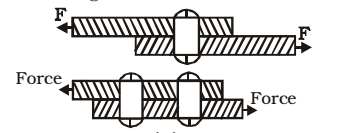
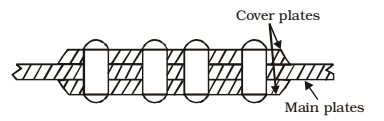
(ii) Butt Joint:
- The butt joint is that in which the plates to be connected butt against each other and the connection is made by providing a cover plate on one or both sides of joint.
- The butt joint may have a single row or staggered or chain riveting.
STEEL STRUCTURES ACE GATE NOTES : CLICK HERE
COMMON TERMS
- Nominal diameter (d) The diameter of the shank of a rivet before riveting, is called the nominal diameter. For a bolt, the diameter of the unthreaded portion of the shank is called its nominal diameter.
- Effective diameter or gross diameter: The effective or gross diameter of a rivet is equal to the diameter of the hole it fills after riveting. For a bolt, the nominal diameter is same as the gross diameter.
- Net area: The net area of a bolt is the area at the root of the thread.
- Gauge: A row of rivets parallel to the direction of force is called a gauge line. The normal distance between two adjacent gauge line is called the gauge.
- Edge distance: It is the distance between the edge of a member or cover plate and the centre of the nearest rivet hole.
- Proof load: Initial tension in HSFG bolts is known as proof load of the bolt.
- Slip Factor: Coefficient of friction in friction type joint is known as slip factor.
- Pitch: The distance between centres of any two adjacent rivets parallel to the direction of force is called pitch. Diagonal pitch is the distance between centres of any two adjacent rivets in the diagonal direction is called diagonal pitch.
DESIGN OF STEEL STRUCTURES STUDY MATERIAL FOR RRB JE PDF CIVILENGGFORALL
DOWNLOAD LINK : CLICK HERE
PASSWORD : CivilEnggForAll
OTHER USEFUL BOOKS
- RAJASTHAN STAFF SELECTION BOARD (RSSB) JUNIOR ENGINEER DIPLOMA CIVIL ENGINEERING EXAM 2022 – HINDI & ENGLISH MEDIUM SOLVED PAPER – FREE DOWNLOAD PDF (CivilEnggForAll.com)
- ISRO TECHNICAL ASSISTANT EXAM 2022 – CIVIL ENGINEERING – HINDI & ENGLISH MEDIUM – SOLVED PAPER – FREE DOWNLOAD PDF (CivilEnggForAll.com)
- MADHYA PRADESH PUBLIC SERVICE (MPPSC) COMMISSION – ASSISTANT ENGINEER EXAM – MPPSC AE 2021 CIVIL ENGINEERING – SOLVED PAPER WITH EXPLANATIONS – PDF FREE DOWNLOAD
- BIHAR PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION (BPSC) ASSISTANT ENGINEER EXAM – 2022 – CIVIL ENGINEERING – SOLVED PAPER – FREE DOWNLOAD PDF (CivilEnggForAll.com)
- ODISHA PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION – OPSC AEE PANCHAYATI RAJ EXAM 2021 – SOLVED PAPER WITH EXPLANATION – FREE DOWNLOAD PDF





















