
CONTENTS
- WATER QUALITY STANDARDS
- WATER TREATMENT
- SCREENING
- PLAIN SEDIMENTATION
- DESIGN OF SEDIMENTATION TANK
- SEDIMENTATION WITH COAGULATION
- JAR TEST
- FILTERATION
- DISINFECTION
- AERATION
- WATER SOFTENING
- MISCELLANEOUS TREATMENT
- PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS

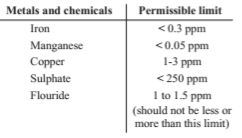
Physical Characteristics of Water
Colour
Measured by
- Comparing colour with standard Nesslar tubes.
- Platinum Cobalt method.
- Tintometer.
Standard permissible limit: 5-20 ppm (in Platinum Cobalt Scale)

ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING IES MASTER GATE MATERIAL : CLICK HERE
Taste and Odour
- Taste is expressed as FTN or Flavor Threshold Number.
- Odour is expressed as TON or Threshold Odour Number.
- Odour is measured by Osmoscope. The number of times the sample is diluted represents TON. Dilution ratio or TON = A+B/A
- where A – volume of raw sample, B – volume of diluted water.
- Standard permissible limit: 1-3. 3.
Temperature : Temperature should be between 10°C and 25°C.
Turbidity
- It may be due to organic or inorganic materials.
- It is measured by different types of turbidity meters or turbidity rod.
- It is expressed in ppm or mg/l of suspended matter. Permissible limit: 5-10 ppm.
Specific Conductivity : To know dissolved salt content, specific conductivity of the water is measured. It is measured by Dionic Water Tester.
WATER TREATMENT
Processes in Treatment of Water
Screening:
- Used to remove bigger floating bodies.
- Screens are kept 45° – 60° inclined to horizontal to increase efficiency.
- Frequently screens are cleaned to avoid clogging.
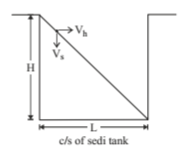
Plain sedimentation
Types of sedimentation tank:
- Intermittent sedimentation tank: Water is kept rest for sometime for setting. It is obsolute now.
- Continuous function sedimentation tank: The length of tank and velocity of travel is designed in such a way that time taken by the particle to travel from one end to another is slightly more than time taken for setting of suspended particle.
Sedimentation with coagulation
The charged colloids present in water repels each other and will not settle in normal sedimentation tank. To overcome this energy barrier, we add chemical compound called coagulants to water. Upon mixing, they form a gelatenous precipitate called flocs, which attracts the fine particles present in water and they increase in mass and settle down easily. Commonly used coagulants are
- hydrated alum (aluminium sulphate) Al2 (SO4) 3. 18H2O commonly known as filter alum.
- ferric chloride.
- copperas (ferrous sulphate + lime).
- ferric sulphate.
- sodium sulphate.
ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING ACE GATE MATERIAL : CLICK HERE
Filteration
Process of passing water through a filter media to remove colloidal particles, bacteria, odour, colour, turbidity, etc.
Types of filters:
- Slow sand filter.
- Rapid sand filter.
- Pressure filter.
Points to be noted:
- Slow sand filters have large plan area than the other two filters.
- Slow sand filters are very good in removing bacteria but not so efficient in removing odour and turbidity and opposite for rapid sand filter.
Disinfection – Disinfection is the process of killing of pathogenic microbes in water.
Methods of disinfection:
Indirect treatment:
- Boiling of water: Can kill germs in water but not future contamination. Used in small scale like household purposes.
- Treatment with ozone: More powerful than chlorine but costly.
- Treatment with UV rays.
Direct method (by addings compounds or chemicals):—
- Treatment with excess lime: More lime is added to water than needed for water softening. It kills bacteria in water but does not take care of future contamination.
- Treatment with potassium permanganate (KMnO4): Used for treatment of water which is contaminated with bacteria in lower concentration. It also oxidise organic matter.
- Treatment with iodine and bromine pills: Provide long lasting protection but costly.
- Treatment with silver: It removes bacteria and algae but is also costly.
- Chlorination.
ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING MADE EASY GATE MATERIAL : CLICK HERE
Aeration
Aeration is the process by which water is brought into contact with air so that it kills bacteria, absorb oxygen removing CO2, H2S, iron and manganese to an extend. Methods of Aeration:
- Using tray aerator.
- Using cascades.
- Using spray nozzles.
- By air diffusion.
- Using trickling beds.
WATER REQUIREMENTS AND TREATMENT STUDY MATERIAL FOR SSC JE PDF CIVILENGGFORALL
DOWNLOAD LINK : CLICK HERE
PASSWORD : CivilEnggForAll
OTHER USEFUL BOOKS
- RAJASTHAN STAFF SELECTION BOARD (RSSB) JUNIOR ENGINEER DIPLOMA CIVIL ENGINEERING EXAM 2022 – HINDI & ENGLISH MEDIUM SOLVED PAPER – FREE DOWNLOAD PDF (CivilEnggForAll.com)
- ISRO TECHNICAL ASSISTANT EXAM 2022 – CIVIL ENGINEERING – HINDI & ENGLISH MEDIUM – SOLVED PAPER – FREE DOWNLOAD PDF (CivilEnggForAll.com)
- MADHYA PRADESH PUBLIC SERVICE (MPPSC) COMMISSION – ASSISTANT ENGINEER EXAM – MPPSC AE 2021 CIVIL ENGINEERING – SOLVED PAPER WITH EXPLANATIONS – PDF FREE DOWNLOAD
- BIHAR PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION (BPSC) ASSISTANT ENGINEER EXAM – 2022 – CIVIL ENGINEERING – SOLVED PAPER – FREE DOWNLOAD PDF (CivilEnggForAll.com)
- ODISHA PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION – OPSC AEE PANCHAYATI RAJ EXAM 2021 – SOLVED PAPER WITH EXPLANATION – FREE DOWNLOAD PDF





















