
CONTENTS
- HYDROLOGY – INTRODUCTION
- FREQUENCY OF RAINFALL
- EVAPORATION
- EVAPOTRANSPIRATION
- INFILTRATION
- HYDROGRAPH
- RUNOFF
- PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS

Hydrologic Cycle
- Balance between precipitation and evaporation is maintained.
- Total water resource on Earth is always constant.
- Sun is main energy source for hydrological cycle.
Rainfall or Precipitation
Mass inflow – Mass outflow = Change in storage (s)
Mass inflow is by precipitation (P)
Mass outflow is by surface runoff (R), ground water net outflow (G), evaporation (E) and transpiration (T)
P-(R+G+E+T) = s
IES MASTER CIVIL GATE STUDY MATERIALS : CLICK HERE
Rain Gauge Density
It is the average area served by a rain gauge, i.e.
Rain Gauge Density = Total Area/Total Number of Rain Gauges
Index of Wetness = Actual Rainfall at a place in 1 year/Normal annual rainfall at that place
FREQUENCY OF RAINFALL
Return Period (T): Average time interval between occurence of rainfall of magnitude greater than or equal to specific magnitude (x).
Excedence Probability (P): The probability of getting a rainfall of magnitude greater than or equal to a specific magnitude. P = 1/T
Similarly, the probability of non-receiving rainfall (q), q = 1 – p
HYDROLOGY ACE GATE MATERIAL : CLICK HERE
EVAPORATION
It is the process by which liquid changes from liquid into solid state below its boiling point.
EVAPOTRANSPIRATION
Transpiration is the loss of water from the plants. It is measured by phytometer. Evapotranspiration is the sum of evaporation and transpiration.
HYDROLOGY MADE EASY GATE NOTES : CLICK HERE
INFILTRATION
During precipitation, a part of the water is absorbed by the soil. This is called infiltration.
HYDROGRAPH
It is the graph of discharge in a stream with time. Rising limb and crest is controlled by basin and storm (rainfall) characteristics while recession limb is entirely controlled by basin characteristics.
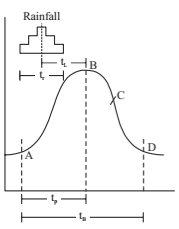
tB – time base t – time till peak p discharge from starting time t r – rainfall duration tL – lag time, i.e. time between centre of mass of rainfall to C.M. of hydrograph AB – rising limb BD – recession club
Base Flow Separation
The base flow is separated from the total storm hydrograph to obtain the relationship between surface flow hydrograph and effective rainfall. The surface runoff hydrograph obtained by base flow separation is called Direct Runoff Hydrograph (DRH).
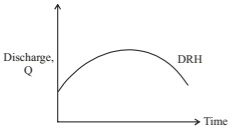
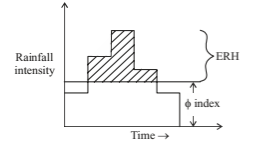
Total area of DRH gives total runoff in that area. When initial losses and infiltration losses are deducted from the hyetograph, Effective Rainfall Hyetograph (ERH) is obtained. Both DRH and ERH represent same quantity but different units.
HYDROLOGY IES MASTER GATE NOTES : CLICK HERE
Unit Hydrograph (UH)
UH is the DRH resulting from one unit depth (1 cm) of rainfall excess occurring uniformly over the basin and at a uniform rate for a specified duration (D). It is called D-hour unit hydrograph.
Basic Assumptions of UH
1. Time Invariance:— The DRH for a given effective rainfall in a catchment is always the same irrespective of when it occurs. 2. Linear Response:— If the rainfall excess in duration D hours is r times the unit depth, the ordinate of the DRH will be equal to r times the ordinate of the corresponding D-h UH.
RUNOFF
The portion of precipitation flowing off from a catchment area through a surface channel is called runoff. Direct Runoff: Water flows through surface and enters a stream. Base Runoff: Water enters stream as ground water, so it takes more time. Runoff Coefficient (k): The portion of rainfall that forms runoff.
k = runoff/rainfall
HYDROLOGY STUDY MATERIAL FOR SSC JE PDF CIVILENGGFORALL
DOWNLOAD LINK : CLICK HERE
PASSWORD : CivilEnggForAll
OTHER USEFUL BOOKS
- RAJASTHAN STAFF SELECTION BOARD (RSSB) JUNIOR ENGINEER DIPLOMA CIVIL ENGINEERING EXAM 2022 – HINDI & ENGLISH MEDIUM SOLVED PAPER – FREE DOWNLOAD PDF (CivilEnggForAll.com)
- ISRO TECHNICAL ASSISTANT EXAM 2022 – CIVIL ENGINEERING – HINDI & ENGLISH MEDIUM – SOLVED PAPER – FREE DOWNLOAD PDF (CivilEnggForAll.com)
- MADHYA PRADESH PUBLIC SERVICE (MPPSC) COMMISSION – ASSISTANT ENGINEER EXAM – MPPSC AE 2021 CIVIL ENGINEERING – SOLVED PAPER WITH EXPLANATIONS – PDF FREE DOWNLOAD
- BIHAR PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION (BPSC) ASSISTANT ENGINEER EXAM – 2022 – CIVIL ENGINEERING – SOLVED PAPER – FREE DOWNLOAD PDF (CivilEnggForAll.com)
- ODISHA PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION – OPSC AEE PANCHAYATI RAJ EXAM 2021 – SOLVED PAPER WITH EXPLANATION – FREE DOWNLOAD PDF





















