
CONTENTS
- Types of irrigation
- Some Important Terms of Irrigation Engineering
- Consumptive use of water
- Evapo-Transpiration
- Water Logging

IRRIGATION
Irrigation may be defined as the process of supplying water to soil for rising crops, or is generally defined as the application of water to soil for supplying the moisture essential for plant growth.
IES MASTER CIVIL GATE STUDY MATERIALS : CLICK HERE
TYPES OF IRRIGATION
- Flow Irrigation: In this irrigation supply of irrigation water available is at such a level that it is conveyed on to the land by the gravity flow.
- Lift Irrigation: In lift irrigation, the water is lifted up by mechanical means. e.g.: Irrigation from well in which sub soil water is lifted up to the surface and is then conveyed to the agricultural field.
CLASSIFICATION OF WATER PRESENT IN SOIL
- Hygroscopic water: It is not capable of movement by the action of gravity or capillary forces.
- Capillary water: It is the part in excess of the hygroscopic water which exists in the pore spaces of the soil by molecular attraction.
- Gravitational water: It is that part in excess of hygroscopic and capillary water which will move out of the soil if favourable drainage is provided.
SATURATION CAPACITY (or Maximum holding capacity/Total capacity)
It is the amount of water required to fill all the pore spaces between soil particles by replacing all air held in pore spaces.
Field Capacity (F.C.)
It is the moisture content of the soil after free drainage has removed most of the gravity water.
IRRIGATION ENGINEERING ACE GATE MATERIAL : CLICK HERE
Permanent Wilting Point /Wilting co-efficient (PWP)
It is the water content at which plants can no longer extract sufficient water from the soil for its growth.
PWP ≈ F.C/ 2.0 to 2.4
Readily available water
It is that portion of available moisture that is most easily extracted by plants and is approximately 75% of the available moisture.
DUTY (D)
Irrigation capacity of a unit of water, or it is the area irrigated in hectares by 1cumec of discharge flowing throughout the base period. {hect/comec}
Delta
It is total depth of water required by a crop during the entire period, the crop is in the field. {cm or m}
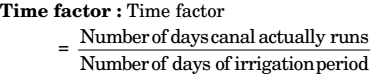

Base period (B)
It is the time interval in days between the first watering given prior to sowing and the last watering before harvesting (Days).
Crop period
It is the time interval between sowing and harvesting of crop (Days)
Relation between Duty and Delta.
Duty = 8.64B/D m
IRRIGATION ENGINEERING ACE GATE NOTES : CLICK HERE
FACTOR AFFECTING DUTY
- Method and system of irrigation
- Mode of applying water
- Method of cultivation
- Time and Frequency of tilling
- Type of crop
- Base Period of crop
- Climatic condition of the area: Temperature, wind, humidity, rainfall etc.
- Quality of water
- Method of assessment
- Canal condition: Earthen canal, Lined canal.
- Character of soil and Sub soil of the canal
- Character of soil and sub soil of the irrigation field

IMPROVING DUTY
- Suitable method of applying water to the crop should be used.
- Land should be properly ploughed and levelled before sowing the crop. It should be given good filth. (structure)
- Land should be cultivated frequently since frequent cultivation reduces loss of moisture, specially when the ground water is within capillary reach of ground surface.
- Canal should be lined. This reduces seepage, percolation losses and evaporation losses also.
- Parallel canal should be constructed so that F.S.L. will be lowered and thus losses will also be reduced.
- Idle length of canal should be reduced.
- Alignment of the canal either in sandy soil or in fissured rock should be avoided.
- Canal should be so aligned that the areas to be cultivated are concentrated along it.
- Source of water should be such that it gives good quality of water.
- Rotation of crops must be practiced.
- Volumetric method of assessment should be used.
- Farmers must be trained in the proper use of water so that they apply correct quality of water at correct timing.
- The land should be redistributed to the farmers so that they get only as much land as they are capable of managing it.
- Research stations should be established to study the soil, the seed and conservation of moisture.
- The canal staff should be efficient, responsible and honest.
CONSUMPTIVE USE OF WATER
It is the total depth of water consumed by transpiration from crop, evaporation from soil and water surface area, including the transpiration from accompanying weed growth. The rain water and dew intercepted by leaves of plants and subsequently evaporating without entering the plant system also from part of consumption use.
IRRIGATION STUDY MATERIAL FOR SSC JE PDF CIVILENGGFORALL
DOWNLOAD LINK : CLICK HERE
PASSWORD : CivilEnggForAll
OTHER USEFUL BOOKS
- RAJASTHAN STAFF SELECTION BOARD (RSSB) JUNIOR ENGINEER DIPLOMA CIVIL ENGINEERING EXAM 2022 – HINDI & ENGLISH MEDIUM SOLVED PAPER – FREE DOWNLOAD PDF (CivilEnggForAll.com)
- ISRO TECHNICAL ASSISTANT EXAM 2022 – CIVIL ENGINEERING – HINDI & ENGLISH MEDIUM – SOLVED PAPER – FREE DOWNLOAD PDF (CivilEnggForAll.com)
- MADHYA PRADESH PUBLIC SERVICE (MPPSC) COMMISSION – ASSISTANT ENGINEER EXAM – MPPSC AE 2021 CIVIL ENGINEERING – SOLVED PAPER WITH EXPLANATIONS – PDF FREE DOWNLOAD
- BIHAR PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION (BPSC) ASSISTANT ENGINEER EXAM – 2022 – CIVIL ENGINEERING – SOLVED PAPER – FREE DOWNLOAD PDF (CivilEnggForAll.com)
- ODISHA PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION – OPSC AEE PANCHAYATI RAJ EXAM 2021 – SOLVED PAPER WITH EXPLANATION – FREE DOWNLOAD PDF





















