

Table of Contents
CONTENTS
- ESTIMATION
- TYPES OF ESTIMATE
- ANALYSIS OF RATES
- CEMENT CONCRETE – RATE ANALYSIS
- RCC WORK – RATE ANALYSIS
- BRICKWORK WITH STANDARD BRICKS
- CEMENT CONRETE FLOOR
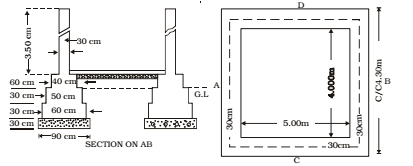
- SEPTIC TANK
- EARTHWORK
- CONCRETE
- BRICKWORK
- WOODWORK
- STEEL AND IRON WORK
- PLASTERING AND POINTING
- PAINTING
- SANITARY AND WATER SUPPLY WORKS
- CENTRE LINE METHOD
- MID SECTION METHOD

ESTIMATE
An estimate is the anticipated or probable cost of work and is usually prepared before the construction is taken up, Before undertaking any work or project it is necessary to know its probable cost which is obtained or derived by estimating. The estimate is prepared by computing or calculating the quantities required and then calculating the cost at suitable rates, to get the expenditure likely to be incurred in the construction of the work or structure.
Different types of estimate are following:-
- Preliminary estimate or approximate or abstract estimate or Rough cost estimate.
- Plinth Area estimate
- Cube Rate estimate or cubical content estimate
- Approximate quantity method estimate.
- Detailed estimate or item rate estimate.
- Revised estimate
- Supplementary estimate.
- Supplementary and Revised estimate.
- Annual Repair or maintenance estimate.
PRELIMINARY ESTIMATE
- It is used to ascertain the actual cost forecast of a project.
- Assist the client in knowing to what extent he needs to be financially committed to a particular project.
- Estimated is also function as the design guide whether the project to the allocation mode either.
IES MASTER CIVIL ENGINEERING GATE STUDY MATERIALS PDF: CLICK HERE
PLINTH AREA ESTIMATE
This is prepared on the basis of plinth area of building, the rate being deducted from the cost of similar building having similar specification, heights and construction in the locality. Plinth area estimate is calculated by finding the plinth area of building and multiplying by the plinth area rate. The plinth area should be calculated for the covered area by taking external dimension of the building at the floor level. Courtyard and other open area should not be included in the plinth area. plinth area estimate is only approximate and is a preliminary estimate, to know the approximate cost beforehand.
CUBE RATE ESTIMATE FOR BUILDING
Cube Rate Estimate is a preliminary estimate or an approximate estimate and is prepared on the basis of the cubical contents of the building. The cube rate being deducted from the cost of the similar building having similar specification and construction in the locality. This is calculated by finding the cubical content of the building(length u breadth u height) and multiplied it by the cube rate. The length and breadth should be taken as the external dimensions of the buildings at the floor levels and the height should be taken from the floor level to top of roof (or half way of the sloped roof).
APPROXIMATE QUANTITY METHOD ESTIMATE
In this method approximate total length of walls is found in running metre and this total length multiplied by the rate per running metre of wall gives a fairly accurate cost. For this method the structure may be divided into two parts viz (i) foundation including plinth and (ii) Superstructure. The running metre cost for foundation and superstructure should be calculated first and these running metre rate should be multiplied by the total length of walls.
DETAILED ESTIMATE OR ITEM RATE ESTIMATE
Detailed estimate is an accurate estimate and consist of working out the quantities of each item of works, and working the cost. The dimensions, length, breadth and height of each item are taken out correctly from drawing and quantities of each item are calculated and abstracting and billing are done.
REVISED ESTIMATE
Revised estimate is a detailed estimate and is required to be prepared under any of the following circumstances:- (a) When the original sanctioned estimate is exceeded or likely to exceed by more than 5% (b) When the expenditure on a work exceeds or likely to exceed the amount of administrative sanction by more than 10%
SUPPLEMENTARY ESTIMATE
Supplementary estimate is a detailed estimate and is prepared when additional works are required to supplement the original work. This is a fresh detailed estimate of the additional works in addition to the original estimate.
SUPPLEMENTARY AND REVISED ESITIMATE
When a work is partially abandoned and the estimated cost of the remaining work is less than 95% of the original work, that is less than 95% of the original sanctioned estimate, or when these are material deviations and changes in the design which may cause substantial saving in the estimate then the amount of the original estimate is revised by the competent authority.
ANNUAL REPAIR OR MAINTENANCE ESTIMATE
Annual Repair or annual maintenance estimate is a detailed estimate and is prepared to maintain the structure or work in proper order and safe condition.
CIVIL ENGINEERING ACE GATE STUDY MATERIAL PDF: CLICK HERE
GLOSSARY OF TECHNICAL TERMS
- Basis of estimate: A document which describes the scope basis, pricing basis, methods, qualifications, assumptions, inclusions and exclusions.
- Bond: Usually refers to a performance bond, which is a security bond issued by an insurance company or a bank to guarantee satisfactory completion of a project by a contractor.
- Construction Cost: The total cost to construct a project. This value usually does not include the preplanning site or right of way acquisition or design costs and may not include start -up and commissioning costs. This total or subtotal is usually identified as such in an estimate report. Also known as total estimated contract cost(TECC).
- Contingency: When estimating the cost for a project, product or services or other item or investment, there is always uncertainty as to the precise content of all items in the estimate, how work will be performed, what work condition will be performed, what work conditions will be like when the project is executed and so on. These uncertainties are risks to the project.
- Cost Index: A value used to adjust the cost of from one time to another. There are various published cost indexes, listed by year, quarter or month. Rs means publishes a historical cost index.
ANALYSIS OF RATES
The determination of rate per unit of a particular item of work from the cost of quantities of materials, the cost of labours and other miscellaneous petty expense require for its completion is known as the analysis of rate. A reasonable profit, usually 10% for the contractor is also included in the analysis of rate. Rates of material are usually taken as the rates delivered at the site of work and include the first cost(Cost at origin), Cost of transport, railway freight, if any taxes etc. If the materials are to be carried from a distant place, more than 8 kms(5miles),then cost of transport is also added. the rates of materials and labour vary from place to place and therefore the rates of different times of work also vary from place to place.
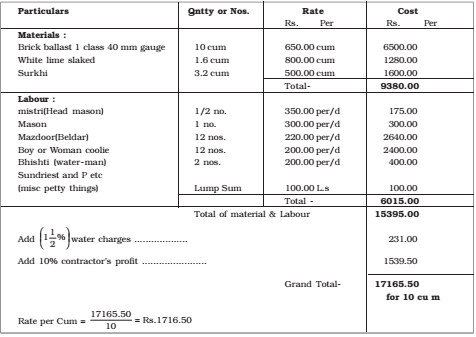
The rates of a particular item of work depends on the following
- Specifications of works and materials, quality of materials, proportion of mortar method of constructional operation etc.
- Quantities of materials and their rates, number of different types of labour and their rates.
- Location of the site of work and its distances from the sources of materials and the rate of transport availability of water.
- Profits and miscellaneous and overhead expenses of contractor.
CIVIL ENGINEERING MADE EASY GATE NOTES PDF: CLICK HERE
Overhead Cost
Overhead cost include general office expenses, rents, taxes, supervision and other costs which are indirect expenses and not productive expenses on the job.
General overhead:
- Establishment
- Stationary, printing, postages, etc.
- Travelling expenses
- Telephone
- Rent and taxes
Job overhead:
- Supervision (salary or engineers, overseers, supervision)
- Handling of materials,
- Repairs, carriage and depreciation of T and P
- Amenities of labour
- Workmen’s compensation insurance, etc
- interest on investment
- Losses on advances.
The analysis of rates is usually worked out for the unit of payment of the particular item of work under two head: (i) Materials and (ii) labour and their costs added together give the cost of the item of work. The costs of materials are taken as delivered at site inclusive of the transport, local taxes and other change. For tools and plants and miscellaneous petty items which cannot be accounted in details lump-sum provision is made. A provision for water charges @1.5% of the total cost is made in rate.
TASK OR OUT – TURN WORK
Task: The capacity of doing work by an artisan or skilled labour in the form of quantity of work per day is known as the task-work or out-turn of the labour. The out-turn of work per artisan varies to some extent according to the nature, size, height, situation, location etc. In bigger cities where specialised and experienced labour is available then the out-turn is greater than small towns and country sides. In well organised work, less labour is required. The following may be taken as the approximate quantity of work or out-turn or task for an average artisan per day.
ESTIMATION AND COSTING STUDY MATERIAL FOR RRB JE PDF CIVILENGGFORALL
DOWNLOAD LINK : CLICK HERE
PASSWORD : CivilEnggForAll
OTHER USEFUL BOOKS
- BUILDING MATERIALS – MOCK TEST 1 (QUICK)
- TELANGANA STATE PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION – ASSISTANT ENGINEER 2023 – TSPSC AE 2023 CIVIL ENGINEERING EXAM SOLVED PAPER WITH EXPLANATIONS PDF FREE DOWNLOAD
- SSC JE 2023 CIVIL ENGINEERING (CPWD/CWC/MES) EXAM SOLVED PAPER PDF FREE DOWNLOAD
- BIHAR PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION ASSISTANT ENGINEER (BPSC AE) 2022 CIVIL ENGINEERING EXAM SOLVED PAPER WITH EXPLANATIONS PDF
- NHPC (NATIONAL HYDROELECTIC POWER CORPORATION) JUNIOR ENGINEER NHPC JE 2022 CIVIL ENGINEERING EXAM SOLVED PAPER PDF FREE DOWNLOAD

Leave a Reply