

Table of Contents
CONTENTS
- Definition of Estimation and Costing
- Lumpsum
- Measurement of Materials and Works
- Types of Estimates
- Abstract of Estimate Form
- Data
- Analysis of Rates
- Detailed Specifications
- Concrete in Foundations
- Cement Concrete
- Introduction, Necessity of Valuation of Building

DEFINITION OF ESTIMATION AND COSTING
- Estimating is the technique of calculating or Computing the various quantities and the expected Expenditure to be incurred on a particular work or project.
- Particularly if the funds available are less than the estimated cost the work is done in part or by reducing it or specifications are altered, the following requirement are necessary for preparing an estimate.
- Drawings like plan, elevation and sections of important points.
- Detailed specifications about workmanship & properties of materials etc.
- Standard schedule of rates of the current year.
REQUIREMENT FOR ESTIMATION AND COSTING
- Estimate give an idea of the cost of the work and hence its feasibility can be determined i..e whether the project could be taken up with in the funds available or not.
- Estimate gives an idea of time required for the completion of the work.
- Estimate is required to invite the tenders and Quotations and to arrange contract.
- Estimate is also required to control the expenditure during the execution of work.
- Estimate decides whether the proposed plan matches the funds available or not.
ESTIMATION AND COSTING STUDY MATERIAL FOR RRB JE EXAM PDF: CLICK HERE
METHOD OF ESTIMATING
Estimating involves the following operations
- Preparing detailed Estimate.
- Calculating the rate of each unit of work
- Preparing abstract of estimate
DATA REQUIRED TO PREPARE AN ESTIMATE
- Drawings i.e., plans, elevations, sections etc.
- Specifications.
- Rates.
Drawings
If the drawings are not clear and without complete dimensions the preparation of estimation become very difficult. So, It is very essential before preparing an estimate.
Specifications
- General Specifications: This gives the nature, quality, class and work and materials in general terms to be used in various parts of woks. It helps to form a general idea of building.
- Detailed Specifications: These gives the detailed description of the various items of work laying down the Quantities and qualities of materials, their proportions, the method of preparation workmanship and execution of work.
Rates
For preparing the estimate the unit rates of each item of work are required.
- For arriving at the unit rates of each item.
- The rates of various materials to be used in the construction.
- The cost of transport materials.
- The wages of labour, skilled or unskilled of masons, carpenters, Mazdoor, etc.,
IES MASTER CIVIL ENGINEERING GATE STUDY MATERIALS PDF: CLICK HERE
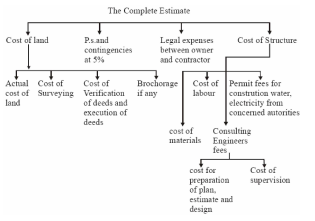
COMPLETE ESTIMATE
Most of people think that the estimate of a structure includes cost of land, cost of materials and labour, But many other direct and indirect costs included and is shown below.
LUMPSUM
While preparing an estimate, it is not possible to workout in detail in case of petty items. Items other than civil engineering such items are called lumpsum items or simply L.S.Items. The following are some of L.S. Items in the estimate.
- Water supply and sanitary arrangements.
- Electrical installations like meter, motor, etc.,
- Architectural features.
- Contingencies and unforeseen items.
In general, certain percentage on the cost of estimation is alloted for the above L.S.Items Even if sub-estimates prepared or at the end of execution of work, the actual cost should not exceed the L.S.amounts provided in the main estimate.
WORK CHARGED ESTABLISHMENT:
During the construction of a project considerable number of skilled supervisors, work assistance, watch men etc., are employed on temporary basis. The salaries of these persons are drawn from the L.S. amount allotted towards the work charged establishment. that is, establishment which is charged directly to work. an L.S.amount of 1½ to 2% of the estimated cost is provided towards the work charged establishment.
MEASUREMENT OF MATERIALS AND WORKS UNITS OF MEASUREMENTS
The units of measurements are mainly categorised for their nature, shape and size and for making payments to the contractor and also. The principle of units of measurements normally consists the following:
- Single units work like doors, windows, trusses etc., are expressed in numbers.
- Works consists linear measurements involve length like cornice, fencing, hand rail, bands of specified width etc., are expressed in running metres (RM)
- Works consists areal surface measurements involve area like plastering, white washing, partitions of specified thickness etc., are expressed in square meters (m2)
- Works consists cubical contents which involve volume like earth work, cement concrete, Masonry etc are expressed in Cubic metres.
RULES FOR MEASUREMENT
The rules for measurement of each item are invaribly described in IS-1200. However some of the general rules are listed below.
- Measurement shall be made for finished item of work and description of each item shall include materials, transport, labour, fabrication tools and plant and all types of overheads for finishing the work in required shape, size and specification.
- In booking, the order shall be in sequence of length, breadth and height or thickness.
- All works shall be measured subject to the following tolerances.
- Linear measurement shall be measured to the nearest 0.01m.
- Areas shall be measured to the nearest 0.01 sq.m
- Cubic contents shall be worked-out to the nearest 0.01 cum
- Same type of work under different conditions and nature shall be measured separately under separate items.
- The bill of quantities shall fully describe the materials, proportions, workmanships and accurately represent the work to be executed. 6. In case of masonary (stone or brick) or structural concrete, the categories shall be measured separately and the heights shall be described:
- from foundation to plinth level
- from plinth level to First floor level
- from Fist floor to Second floor level and so on.
ACE ACADEMY CIVIL ENGINEERING GATE STUDY MATERIALS PDF: CLICK HERE
METHODS OF TAKING OUT QUANTITIES
The quantities like earth work, foundation concrete, brickwork in plinth and super structure etc., canbe workout by any of following two methods:
- Long wall – short wall method
- Centre line method.
- Partly centre line and short wall method.
Long wall-short wall method
In this method, the wall along the length of room is considered to be long wall while the wall perpendicular to long wall is said to be short wall. To get the length of long wall or short wall, calculate first the centre line lengths of individual walls. Then the length of long wall, (out to out) may be calculated after adding half breadth at each end to its centre line length. Thus the length of short wall measured into in and may be found by deducting half breadth from its centre line length at each end. The length of long wall usually decreases from earth work to brick work in super structure while the short wall increases. These lengths are multiplied by breadth and depth to get quantities.
Centre line method
This method is suitable for walls of similar cross sections. Here the total centre line length is multiplied by breadth and depth of respective item to get the total quantity at a time. When cross walls or partitions or verandah walls join with mainhall, the centre line length gets reduced by half of breadth for each junction. such junction or joints are studied caefully while calculating total centre line length.The estimates prepared by this method are most accurate and quick.
Partly centre line and partly cross wall method
This method is adopted when external (i.e., allround the building) wall is of one thickness and the internal walls having different thicknesses. In such cases, centre line method is applied to external walls and long wall-short wall method is used to internal walls. This method suits for different thicknesses walls and different level of foundations. Because of this reason, all Engineering departments are practicing this method.
DETAILED ESTIMATE
The preparation of detailed estimate consists of working out quantities of various items of work and then determine the cost of each item. This is prepared in two stages.
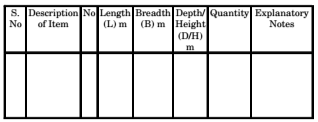
Details of measurements and calculation of quantities
The complete work is divided into various items of work such as earth work concreting, brick work, R.C.C. Plastering etc., The details of measurements are taken from drawings and entered in respective columns of prescribed proforma. the quantities are calculated by multiplying the values that are in numbers column to Depth column as shown below:
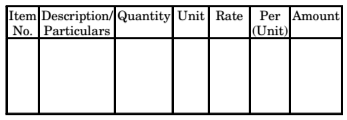
Abstract of Estimated Cost
The cost of each item of work is worked out from the quantities that already computed in the details measurement form at workable rate. But the total cost is worked out in the prescribed form is known as abstract of estimated form. 4% of estimated Cost is allowed for Petty Supervision, contingencies and Unforeseen items.
The detailed estimate should accompanined with
- Report
- Specification
- Drawings (plans, elevation, sections)
- Design charts and calculations
- Standard schedule of rates.
METHODS OF PREPARATION OF APPROXIMATE ESTIMATE
Preliminary or approximate estimate is required for studies of various aspects of work of project and for its administrative approval. It can decide, in case of commercial projects, whether the net income earned justifies the amount invested or not. The approximate estimate is prepared from the practical knowledge and cost of similar works. The estimate is accompanied by a report duely explaining necessity and utility of the project and with a site or layout plan. A percentage 5 to 10% is allowed for contingencies. The following are the methods used for preparation of approximate estimates.
- Plinth area method
- Cubical contents methods
- Unit base method.
MADE EASY CIVIL ENGINEERING GATE NOTES PDF: CLICK HERE
Plinth area method
The cost of construction is determined by multiplying plinth area with plinth area rate. The area is obtained by multiplying length and breadth (outer dimensions of building). In fixing the plinth area rate, carefull observation and necessary enquiries are made in respect of quality and quantity aspect of materials and labour, type of foundation, height of building, roof, wood work, fixtures, number of storeys etc., As per IS 3861-1966, the following areas include while calculating the plinth area of building.
- Area of walls at floor level.
- Internal shafts of sanitary installations not exceeding 2.0m2, lifts, airconditioning ducts etc.,
- Area of barsati at terrace level: Barsati means any covered space open on one side constructed on one side constructed on terraced roof which is used as shelter during rainy season.
- Porches of non cantilever type.
Areas which are not to include
- Area of lofts.
- Unenclosed balconies.
- Architectural bands, cornices etc.,
- Domes, towers projecting above terrace level.
- Box louvers and vertical sunbreakers.
Cubical Contents Method
This method is generally used for multistoreyed buildings. It is more accurate that the other two methods viz., plinth area method and unit base method. The cost of a structure is calculated approximately as the total cubical contents (Volume of buildings) multiplied by Local Cubic Rate. The volume of building is obtained by Length x breadth x depth or height. The length and breadth are measured out to out of walls excluding the plinth off set. The cost of string course, cornice, carbelling etc., is neglected. The cost of building = volume of buildings x rate/ unit volume.
Unit Base Method
According to this method the cost of structure is determined by multiplying the total number of units with unit rate of each item. In case schools and colleges, the unit considered to be as ‘one student’ and in case of hospital, the unit is ‘one bed’. the unit rate is calculated by dividing the actual expenditure incurred or cost of similar building in the nearby locality by the number of units.
ESTIMATION AND COSTING STUDY MATERIAL FOR SSC JE PDF CIVILENGGFORALL
DOWNLOAD LINK : CLICK HERE
PASSWORD : CivilEnggForAll
OTHER USEFUL BOOKS
- BUILDING MATERIALS – MOCK TEST 1 (QUICK)
- TELANGANA STATE PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION – ASSISTANT ENGINEER 2023 – TSPSC AE 2023 CIVIL ENGINEERING EXAM SOLVED PAPER WITH EXPLANATIONS PDF FREE DOWNLOAD
- SSC JE 2023 CIVIL ENGINEERING (CPWD/CWC/MES) EXAM SOLVED PAPER PDF FREE DOWNLOAD
- BIHAR PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION ASSISTANT ENGINEER (BPSC AE) 2022 CIVIL ENGINEERING EXAM SOLVED PAPER WITH EXPLANATIONS PDF
- NHPC (NATIONAL HYDROELECTIC POWER CORPORATION) JUNIOR ENGINEER NHPC JE 2022 CIVIL ENGINEERING EXAM SOLVED PAPER PDF FREE DOWNLOAD

Leave a Reply