
Table of Contents
IES MASTER GATE MATERIAL
PERT CPM AND CONSTRUCTION EQUIPMENT
GATE – PSU – IES – GOVT EXAMS – STUDY MATERIAL
FREE DOWNLOAD PDF


CONTENTS
- PROJECT MANAGEMENT
- FUNDAMENTALS OF NETWORK
- PROGRAMME EVALUATION REVIEW TECHNIQUES
- CRITICAL PATH METHOD
- CRASHING
- UPDATING AND RESOURCE ALLOCATION
- A-O-N DIAGRAM
- ENGINEERING ECONOMY
- FUNDAMENTALS OF EQUIPMENTS
- EVACUATION EQUIPMENT
- LOADING AND CONVEYING EQUIPMENT
- HOISTING EQUIPMENTS
- CONCRETING EQUIPMENT
- COMPACTING EQUIPMENT
- CONSTRUCTION EQUIPMENT OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
INTRODUCTION :
What is Project Management?
INTRODUCTION :
- At one point or another, almost every organization will take on a large and complex project. A construction company putting up an office building or laying a highway must complete thousand of costly activities.
- Almost every industry worries about how to manage similar large-scale, complicated projects effectively.
- Large, often one-time, projects are difficult challenges to operations managers. The stakes are high. Millions in cost overruns have been wasted due to poor planning on projects. Unnecessary delay have occurred due to poor scheduling. And companies have gone bankrupt due to poor controls
- Here comes the role of project management, as project organisations are set up to handle such job and are often disabled when the project is complete.
- Project management is the art of organizing the components of a project, whether the project is development of a new product, the launch of a new service, a marketing campaign, or a wedding
- Project management increases the productivity through technological innovations taking into considerations the human factor involved in these activities

What are the objectives of Project? Lets see.
- The project should be completed in minimum time period
- Project should use available manpower and local resources as far as possible
- Project should be completed without delay and minimum investment cost.
What are the Elements of Project Management?
Elements of Project Management :
Three stages of project management are:
Planning : Planning is the most important technique of the project management. Planning means defining the objectives of the project and to identify the different task,material, equipment and etc. that are required for completing the project.
Scheduling : Scheduling is the deciding the phasing rate of activities with the starting and completion date and the sequential relationship among the various activities in a project such that work can carried out in an orderly and effective manner. In simple words we can say that scheduling is deciding the order of all the activities and allocation of resources (like time, space, equipment, material and manpower) to the activities.
Whatever the approach taken by a project manager, project scheduling serves several purposes :
- It the relationship of each activity to other and the whole project
- It identifies the precedence relationship among activities
- It encourages the setting of realistic time and cost estimates for each activity
- It helps make better use of people, money, and material resources by identifying critical bottle necks in the project
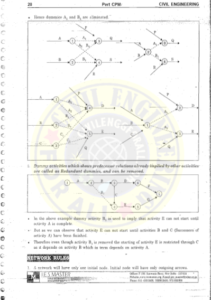
Controlling :
- The control of large projects, like the control of any management system, involves close monitoring of resources, costs, quality and budgets.
- Control also means using a feedback loop to revi project plan and having the ability to shift resources to where they are needed most
- Controlling is complimentary to planning
- Thus the process of controlling involve comparing the progress of work with the schedule at regular intervals and then taking corrective measures to get the desired result, if running behind the schedule
- In simple words we can say controlling involves the execution of planning and scheduling it also deals with the rescheduling of the project.
What are the Methods of Project Management?
METHODS OF PROJECT MANAGEMENT :
- Bar charts or Gantt charts
- Milestone charts
- Network analysis.
Bar charts :
- Bar charts were introduced by Henery Gantt around 1900 A.D., therefore they are also AS Gantt charts.
- Bar chart is a graphical representation of activity vs time.
- Usually horizontal axis represents the time duration and vertical axis represents activities to be performed Activities are shown with the help of a bar.
- The beginning and end of each bar show the”time of start” and”time of finish” of a respectively Therefore the length of the bar represents the time required for the completion of that activity

Advantage of Bar Chart
- It is simple to draw, easy to understand and can be drawn quickly
- No trained/skilled personnel are required to make the chart
- The progress achieved at site is expressed in terms of percentage
- It may be used for depicting the resource requirement of a construction project. It provides a visual representation of the entire project which shows exactly when each of the above activities is supposed to start and finish.
Limitations of Bar Chart
Lack of Degree of Details
- In case of big projects only major activities can be shown, if all the activities of big project are shown on the bar chart then it may become too clunsy.
- Therefore bar charts are not preferred for big projects.
- An activity is represented as a bar, without any details of sub-activities contained in it due to these effective control over activities can not be done. For example consider activity in the below bar chart Laying of pipe work’ is shown as a bar. but following sub activities controls the satisfactorily and timely completion of the activity
Milestone Charts : The milestone chart is a improvement over the original bar chart. In each activity, there are certain key events which mark the completion of certain portion of the main activity. Such key events are called as milestones.
- Milestone can be represented by a arrow, square or a circle on the bar of that particular activity Each milestone can be considered to be specific event along the main activity and this chart is called as milestone chart
- It has been observed that when a particular activity represented by a bar very long.
- The details of sub-activities will be lacking.
- If this activity is broken down into number of subactivities or key events each one of which be recognised during the progress of that activity, and through which controlling can be achieved.

Network Analysis :
Network is a graphical and logical model or plan which lists out the sequence of various a interdepencies) which are required for the completion of project.
Network Analysis Advantages :
- It clearly shows interrelationsnip between various activities and events.
- It can be used for high and complicated projects having large number of activities.
- It is helpful in rescheduling and controlling as its directly indicates the time required in between two milestone or activities.
- It can also be used for projects or activities having uncertainty.
- In case of uncertainties in network diagram allows the use of theory of probability for the estimation of time.
Types of Networks Activity :
- Activity on Arrow(A-O-A) or Arrow Diagrams
- Activity on Node(A-O-N) or Precedence Diagram
- Choice of Network Type Precedence networks(A-O-N) are more widely used where repetitive tasks are involved and where overlapping and interdependencies of activities are major feature of project.
- Activity over Arrows are considered better for the representation of complex projects where there is not a high degree of repetitive work
What is PERT?
Programme Evaluation Review Technique
INTRODUCTION :
- Pert was developed by the U.S Navy during the late 1950’s to accelerate the development of the Polaris Fleet Ballistic Missile PERT,
- PERT, is abbreviated form which stands for Programme Evaluation and Review Technique used for planning, scheduling and monitoring the project.
- Development of this weapon involved the coordinations of the work of private contract management consulting firm and Lockheed Missile system Division
- Coordination with the help of PERT was so successful that the entire project was complete years ahead of schedule.
TIME ESTIMATES:
- A project is composed of many diversified activities which contribute to its completion.
- An important characteristics of any project js its duration.
- As its effect and economy is often dependent on the project duration.
- Total project duration depends on the time taken by each activity Estimation of time required for any activity requires wide experience of similar activities.
Estimation of these time estimates can be done in two ways
1. Deterministic approach : Planner has enough knowledge about the activity and gives a single estimate of the duration which is almost accurate
2. Probabilistic Approach : Planner does not have much idea about the activity as there is little or no past history about it.
- The limits with which the duration will lie, is estimated.
- Pert follows the probabilistic approach and absorbs the uncertainties into the time estimates for activity and project durations.
- Therefore pert is well suited for those projects where there is insufficient or no background information for estimation of time duration
- PERT is used in R&D type projects such as space industry, defence industry etc. As such projects are of non repetitive type or once-through type for which correct time estimates cannot be made.
- Further a Pert analysis is event oriented i e in this analysis interest is more focussed on the Pert (start or completion of activity) rather than the activities.
In order to take into account the uncertainties involved in the activity times three kinds of time estimates are made for each activity in PERT
1. Optimistic time estimate(to)
2. Pessimistic time estimate(tp).
3. Most likely time estimate(tm)
1. Optimistic Time Estimate(to) : It is the minimum time required for an activity if everything goes perfectly well without any problems or adverse conditions developed during the execution of the activity
In this time estimate no provisions are made for delays or setbacks and better than normal conditions are assumed to prevail during the execution of the activity
2. Pessimistic Time Estimate(tp) It is the maximum time required for an activity if everything goes wrong and abnormal situations prevail
This time estimate does not include the possible effects of major catastrophes such as flood earthquakes, fire, labour strikes etc
3. Most Likely time Estimate(tm)
It is the time required to complete the activity if normal conditions prevail
This time estimate lies between pessimistic and optimistic time estimates
What is Critical Path Method ?
INTRODUCTION :
- Critical path method, commonly abriviated as CPM, it closely resembles PERT in any aspects, but it was independently developed M.R. Walker and J E. Kelley of Ramination were involved in development of CPM for the construction of chemical plants in united states.
- Both CPM and PERT are the tools used now a days synonymously for planning, scheduling and controlling of various projects, through broad difference exists between them
- The major difference between the two techniques is that CPM does not incorporate uncertainties in ob times i.e. time estimate is deterministic.
- It assumes that activity times are proportional to the amount of resources allocated to them, and by changing the level of resources the activity times and the project completion time can be varied
- CPM is mostly used in construction projects when there is prior experience in handling similar projects from which relationships between resources and job time are available CPM then evaluates the trade off between projects and project
- For any project the two important aspects to be considered are, the project time and cost. Project times are determined by locating the critical and subcritical paths in the network. It is observed that in construction projects, time is related to project cost, but this relationship is not linear.
- To find the minimum cost, a cost model/time cost relationship/project cost function
- The cost model shows”relationship of the cost” versus”the completion time”.
- Its chord represents the cost and the abscissa has a time scale as shown in the figure below.
- During the formulation of cost model, the direct and indirect costs and the financial resulting from early completion are considered
- Project time corresponding to minimum value of the cost function gives the most optimized duration of the project
What are the Fundamental of Equipments?
INTRODUCTION :
- Construction equipments are one of the very important resource of modern-day construction, mainly in infrastructure projects
- In such projects equipments are used for most of the works including earth moving operation, aggregate production, concrete production and its placement etc.
- In fact, we cannot think of any major construction activity without the involvement of construction equipment.
- There are types of construction equipments suitable for different activities in a construction project.
- The selection of construction equipment defines the construction method, which in a way leads to the determination of time and cost for the project.
- For selecting the right equipment to perform a specific task at the least cost, it is essential to know the features of a construction equipment including its rate of production and the associated cost to operate the equipment.
- While dealing with the construction stage, selection of the most suitable equipment is typical problem which is generally faced by the construction engineers or contractors.
- A contractor may not afford to have all types or sizes of equipment which are required for necessary of the projects Choice is made after considering many factors like nature of the project, cost of equipment depreciation, possibility of its future uses on other projects, its ale value after certain period the saving expected from the use of such equipments etc
CLASSIFICATION OF CONSTRUCTION EQUIPMENT :
Construction equipments can be classified into many ways.
Basis of function of equipment for example, material loading function, material tr function etc. On the basis of functions equipments can be grouped into (a) Power Units(b) Prime movers(c) Tractors(d) Material-Handeling equipment(e) Material processing equipment
Basis of Operation of equipment: Equipments used for moving, and loosening the materials found in their natura pumps, excavators, earth moving, trenchers, compressors etc. Equipments used for processing the materials, for example aggregate, concrete a production. Equipments used for transporting the processed materials Equipments used for placing finish materials. sis of purpose of equipment. General Purpose Earthwork equipment, Hoisting, Concreting, Special equipments Piling rig, coffer dams, tunnel boring machine, caissons eq etc.
SELECTION OF CONSTRUCTION EQUIPMENT :
- For speedy and ecooomic construction of a project, proper choice of equipment is primary importance. The problem of proper selection is further complicated because of the wide range of equipment commercially available Following factors.must be considered before ha a final choice.
- Use of Existing Equipment : When the full utilization of new equipment for the future projects is uncertain, it may be desirable to use existing old equipment even if ita operation is somewhat more expensive Depreciation cost of the new machine is likely to be high, and this would raise the owning cost of the equipment and hence the unit cost of work
- Availability of the Equipment : The equipment which is easily available in the market should be selected for the purpore because any delay in delivery may increase the construction cost repairing of such equipments will also be done easily
- Use of Standard Equipment : Standard equipment is commonly manufactured in large numbers and hence these are readily available and moderately priced Spare parts of standard equipment are easily available and are less costly After the work is over.Selling off standard equipment and its spare part is generally easier than in comparison to non-standard or specialized equipment
- Country of Origin suggestible to buy equipment from own country because this will decrease the repair cont and downtime cost and at the same time it will boost up nation’s economy For imported equipment, it is preferable to import from a soft currency rather from a hard currency country, to have foreign currency reserves
- Suitability for Future Use : If a machine is required only for some part of its use full life, then ways to disposed off or its deployment on some other site should be considered. obsolescence of the machine should not be overlooked.
- Suitability for Site Conditions : The equipment chosen should suit the conditions of the job, soil, valley, working conditions and climate of the region.
- Size of Equipment : Larger equipment give higher outputs on full load, but its cost of production is usually greater than that of smaller units working on partial load.
- For larger equipment transportation to site is generally difficult and costly in comparison to smaller equipment
- Servicing, maintenance and repair facilities have to be greater for larger units. However, larger machines are usually more suitable for tough working conditions Standby cost of larger size equipment is more than, that of smaller equipment
- Versatility possible the in machine selected should be able to do more than one function.and should be inter convertible where ever possible
- Suitability of Local Labour : The locally available operators and technicians should be able to handle the selected equipment. Special equipment may have excellent performance but may be difficult to get repair during break down
DOWNLOAD LINK : IES MASTER PERT CPM and Construction Equipment Study Material for GATE PSU IES GOVT EXAMS Free Download PDF
DISCLAIMER : THIS WEBSITE IS NOT THE ORIGINAL PUBLISHER OF THIS BOOK ON NET. THIS E-BOOK HAS BEEN COLLECTED FROM OTHER SITES ON INTERNET. ALL THE RIGHTS ON THIS BOOK BELONGS TO IES MASTER ACADEMY.

Leave a Reply