
Table of Contents
IRRIGATION
GATE IES PSU’s – STUDY MATERIAL
ACE ENGINEERING ACADEMY FREE DOWNLOAD PDF

- SUBJECT : IRRIGATION- THEORY AND WORKED OUT EXAMPLES, SELF AND CLASSROOM PRACTICE QUESTIONS
- PUBLISHERS : ACE ENGINEERING ACADEMY
- IDEAL FOR : GATE & PSUs – CIVIL ENGINEERING
- EDITION : 2014
- AUTHORS : SUBJECT EXPERTS OF ACE ENGINEERING ACADEMY, HYDERABAD
CONTENTS
- Water Requirements of crops
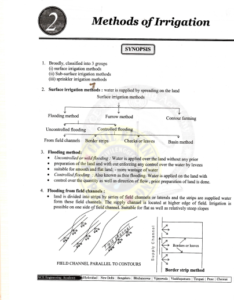
- Methods of Irrigation
- Gravity Dams
- Spill Ways
- Diversion of Head Works
- Design of Unlined Alluvial Canals by silt Theories
- Water Logging and Drainage
- Quality of Irrigation Water and Sodic soils

BRIEF INTRODUCTION – IRRIGATION ACE GATE MATERIAL
1. The loams are ideal soils for irrigation, which posses good water holding capacity, good drainage and aeration characteristics
2. Saturation capacity: It is the total water content of a soil when all the pores of the soil are filled with water
3. Field capacity (FC): It is the maximum amount of water content which can be held by soil against gravity. It is the upper limit of capillary water or the water content available to the plant roots
4. Permanent wilting Point (PWP): It is the water content in a soil when plants become permanently wilted. This value is 2% for sand soil, and 30% for clayey soils.
5. Ultimate wilting Point (UWP): It occurs piants are completely wilted i.e, die away. It is similar to hygroscopic coefficient
6. Available moisture : It is the difference in water content of the soil between the field capacity and the permanent wilting point.
7. Readily available moisture: It is that portion of the available moisture, which is most easily extracted by plant roots. About 75% the available moisture is usually readily available
 Crop Period: Total time elapses between the sowing of the crop and its harvesting.
Crop Period: Total time elapses between the sowing of the crop and its harvesting.
Base period Total time between the first watering done for the preparation of the land for sowing of a crop and the last watering done before its harvesting. Thus crop period is slightly more than the base period for any crop
Duty D – It is defined as the area of land in hectares which can be irrigated for growing any crop if one cumec of water is supplied continuously to the land for the entire base period of crop.
Duty of water increases as one moves from the head of the canal system to the field and hence the place at which duty of water is measured must be specified. In order to state the duty of water in a precise way it is essential to state (i) The base of duty of water and (ii) Place of measurement of duty of water
Base of duty of water: It is the period to which duty of water has reference
Paleo irrigation (Paleo): It is watering done prior to the sowing of a crop
Kor watering: The first watering after the plants have grown a few cm high
Outlet factor: Duty of water at the canal outlet
One cumec day: 8.64 hectare meters, it is a volumetric unit. It is the total volume of water supplied @ 1 cumec in a day
Consumptive use or to plants (Cu) It is the total loss of water due transpiration from the land Lysimeter is used to measure Cu
a) Water conveyance efficiency is the ratio of quantity of water delivered to the field to the quantity of water diverted into the canal system from reservoir
b) Water application efficiency – It is the ratio of quantity of water stored in the root zone of the plants to the quantity of water delivered to the field.
c) Water use efficiency – It is ratio of the quantity of water used beneficially including the water required for leaching to the quantity of water delivered
d) Water storage efficiency : Ratio of quantity of water stored in the root zone during irrigation to the quantity of w needed to bring water content of the soil to field capacity
e) Consumptive use efficiency: Ratio of normal consumptive use of water to the amount of water depleted from the root Zone.
Irrigation Requirements of crops
a) Consumptive requirement irrigation (CIR): It is the amount of water required to meet the evapotranspiration needs of a crop
b) Net irrigation requirements : Amount of irrigation water required to be delivered at the field to meet evapotranspiration and other needs such as leaching
DOWNLOAD LINK : GATE & PSU’s – IRRIGATION- CIVIL ENGINEERING – ACE ENGINEERING ACADEMY STUDY MATERIAL – 2014 EDITION – FREE DOWNLOAD PDF
DISCLAIMER : THIS WEBSITE IS NOT THE ORIGINAL PUBLISHER OF THIS BOOK ON NET. THIS E-BOOK HAS BEEN COLLECTED FROM OTHER SITES ON INTERNET. ALL THE RIGHTS ON THIS BOOK BELONGS TO ACE ENGINEERING ACADEMY.

Leave a Reply