

Table of Contents
CONTENTS
- Indian Railways
- General Science
- Computers
- Indian Panorama
- World Panorama
- Indian History
- Indian Polity
- Economy
- Geography
- Ecology and Environment
- Art, Culture and Tourism
- Environmental Issues concerning the World and India
- Sports
- General Scientific and Technological Development
- MCQ’s for Railways and General Knowledge

INDIAN RAILWAYS
INTRODUCTION TO RAILWAYS
- Considered as the lifeline of the nation the Indian Railways reflects the general state and mood of our country.
- Railways are the principal mode of transportation for freight and passengers in India.
- It conducts multifarious activities like business, sightseeing, pilgrimage along with transportation of goods over longer distances.
- Apart from an important means of transport the Indian Railways have been a great integrating force for more than 150 years.
- It binds the economic life of the country as well as accelerates the development of the industry and agriculture.
- The Indian Railways is an Indian state-owned enterprise, owned and operated by the Government of India through the Ministry of Railways.
- It is one of the world’s largest railway networks comprising 115,000 km and 7,113 stations.

HISTORICAL DEVELOPMENT
The first proposals for railways in India were being debated in Great Britain in the 1840s and the people there started entering into lobbying in support of these proposals by banks, traders, shipping companies etc. The businessmen of England had a strong interest in seeing railways be formed in India. But they wanted the British Parliament to create a Guarantee System.
In the Guarantee System, any company that constructed railways in India was guaranteed a certain rate of interest on its capital investment. This guarantee was to be honoured by the East India Company which then controlled large parts of India. The railways which were made on this arrangement were called Guaranteed Railways. The guarantee was for a return of 5% annually, and the right for the railway company to pull out of the venture and get compensation from the government at any time. Thus, Indian Railways started on a Guarantee System.
IES MASTER CIVIL GATE STUDY MATERIALS : CLICK HERE
- On 27th Sept, 1825 the first rail engine ran from Darling to Stockton in England.
- In the year 1843, Lord Dalhousie first conceived the possibility of opening up of India by means of railway communication. He had proposed to link the three ports of Bombay, Calcutta and Madras by a railway.
- In May, 1845 or about 20 years after construction of first rail road in England, the East Indian Railway Co. was founded. The managing director of this company Mr. R. McDonald Stephenson can be considered the founder of the company. He was the first person to have introduced the idea of rail roads in India and vigorously advocated the construction of East Indian Lines from Howrah to Delhi via Mirzapore.
- After a visit to India in 1845 Stephenson made a proposal to the Court of Directors of East India Company for building a rail line from Calcutta to Burdwan. East India Co. considered this a “wild proposal”. However, with Lord Dalhousie, the then Governor General of India, actively supporting the cause of the Railways for administrative reasons, the Court of Directors of East India Co. finally signed an agreement on 17th August,1849 with EIR for construction of a short experimental line. The main provision was that the company should be economically viable. On August 1, 1849, the Act to incorporate the Great Indian Peninsula Railway was initiated.
- Initially 2 companies were established to develop Railways in India: East India Railway company (1845), Great Indian Peninsular Railway Company (August 1, 1849).
- Another company The Madras Railway Company (MR) was formed provisionally in July 1852 to acquire lands in the “East Indies” and to construct and work a railway or railways in that territory.
- The first Indian Railway started during Lord Dalhousie’s time that on April 16, 1853 at 3:35pm with 14 railway carriages and 400 guests left Bombay’s Bori Bunder for Thane, with a 21-gun salute.
- The first train covered a distance of 34km between Mumbai and Thane. This train was run by the Great Indian Peninsula Company of Central Railway.
- The name of the first rail engine was ‘Beauty.’
- The three locomotives were Sindh, Sultan, and Sahib. This 75 minutes journey was the first Journey of Indian Railway that embarked an era of development thereafter. But this was a passenger service.
- Prior to this there is a trace of Railway in India. In 1851, a steam loco, Thomason, was used for transporting construction material in Roorkee for the Solani viaduct, which was a part of the construction in the Salony Valley.
- The locomotive Thomason was assembled on the spot from parts transported from Calcutta. Second locomotive to arrive in India was Falkland (named for a governor of Bombay), used by the contractors of the GIPR for shunting operations on the first line out of Bombay that was being built.
- In 1854, second train ran between Hoogly and Howrah.
- Meter gauge started functioning in 1870.
- In the first stage, railway was run by private sector, since Indian British Government did not have fund.
- Lord Salisbury had issued three instructions regarding construction and expansion of Indian railways in the states.
- Guarantee system in railway started in 1882.
CHRONOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENT OF INDIAN RAILWAYS
1844: First proposals for the construction of Railways in India were submitted to East India Company by R.M. Stephenson, a Railway Engineer in British India.
1849: East India company undertakes a construction of a 160 km Railway line from Calcutta to Mirzapur. 1850: Contract undertaken by Indian Peninsular Railway for construction of a line from Bombay to Kalyan.
1853: First Railway line between Boribunder (Bombay VT) and Thane (32 km) opened. 1854: First train between Howra and Hoogly (39 km) was run.
1855-60: Following eight Railway companies were established in India.
- Great Indian Peninsula Railway
- The East Indian Railway
- The Madras Railway
- The Bombay-Baroda and Central India Railway
- The Scindia Railway
- The Eastern Bengal Railway
- The South Indian Railway
- The Calcutta and South Eastern Railway
1862: Assistance was given to Railways to construct feeder lines in Northern India
1866: Completion of line from Calcutta to Delhi. This included Son Bridge and Rail cum-Road bridges over Yamuna in Naini and Delhi.
1867: Completion of Bombay-Bhusaval-Itarsi-Jabalpur route of the GIP Railway and connecting it to East India Railway at Naini.
1869-1881: Government took over construction of Railway lines and stopped giving any fresh contract to companies. Disastrous famines occurred during 1874- 79 demanded rapid expansion of Railways
1871: A selection committee of British Parliament was appointed to review the schemes of Railway construction. 1879: Total length of Railway line goes to 14920 km.
1880: The Famine Commission recommended construction of 8000 km of Railway lines in India to protect the country from famine.
1881: Lord Hardington, Secretary of State for India, formulated rules for construction of Railways. He divided Railways into 3 categories (i) productive (ii) unproductive and (iii) protective.
1881-97: New Contracts were given to the following new companies:
- Bengal Central Railway
- The Bengal North Western Railway
- The Rohilkhand and Kumaon Railway
- The Southern Mahratta Railway
- The Indian Midland Railway
- The Bengal Nagpur Railway
- The Assam Bengal Railway Company
- The Burma Railway Company
1890: Passing of the Indian Railways Act which came into force on 1st May 1890.
1900: Total length of Railway line goes to 39,603 km with capital outlay of 329 crores.
1901: Mr. Thomas Robertson was appointed to investigate into railway administration, organization and system.
1902: Setting up of Indian Railways Conference Association to frame or modify rules and regulations of interchange of traffic between Railways.
1905: A Railway Board was established with one President and two members under the Department of Commerce and Industries. Railways branch of the Public Works Department abolished.
1907: Mckay Committee was appointed to examine the financial problems of Railways.
1908: Railway Board was reorganized.
1914: Total length of Railway line goes to 56,456 km with capital outlay of 495 crores.
ACE CIVIL ENGINEERING GATE STUDY MATERIALS : CLICK HERE
1914- 21: World War I period saw Railway fares increasing considerably. Some lines of strategic importance were constructed.
1920: “Indian Railway Enquiry Committee” was appointed under the chairmanship of Sir William Acworth to look into Railway policy, financial and administrative. The report of this Committee laid the foundation of the State management and State control of the Indian Railways.
1922: The Railway Board was reorganized.
1923: Nationalization of Railways started.
1924: As recommended by Railway Finance Committee, headed by Sir Malcolm Hailey, the Railway finances were separated from the General budget by a “Separation Convention”.
1925: Government took over the management of East Indian and Great Indian Peninsula Railways. First Electric Traction was introduced from Bombay VT to Kurla and local train system from Bombay to Kurla started.
1929-30: Route Kilometrage gone up to 66,358 and capital investment gone up to 857 crores.
1930-31: Great Economic depression. Rs. 11 Crore was withdrawn from the Railway Reserve Fund for general revenues.
1937: Burma was separated from India due to which total railway Kilometrage was curtailed by 3200 km.
1939: Total Railway Kilometrage stands at 65850 km.
1939-47: World War II. Due to extensive usage of wagons for military movements very few were left out for private use.
1942: War Transport Board was created.
1943-44: Bengal famine period.
1947-48: Indian Railways suffered great loss during partition of India.
1949-50: Government acquired control over all Railways except a very few private companies. Prior to integration of princely states there were 21 Railways operated by Government of India and Princely States.
1950: Regrouping of Railways was done and 6 Railway zones were formed as follows.
- Indian Railways was Nationalised in 1951.
- The country’s first railway, built by the Great Indian Peninsula Railway.
- It is the biggest employer in the world and the largest single undertaking in the country.
- It has the second biggest electrified system in the world after Russia.
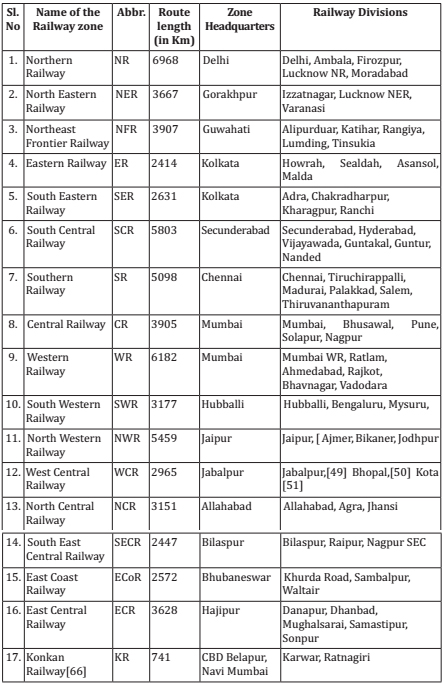
- Indian Railways is divided into 17 zones. Each zone is headed by a general manager.
- The first diesel engine in India ran in 1957.
- At present, diesel engines are manufactured in Varanasi.
Progress of Locomotives
- First locomotive factory was set up in Chittaranjan of West Bengal. This Industrial coach factory was based on the model of Switzerland.
- 1893: First railway foundry was set up at Jamalpur (Bihar).
- 1895: First locomotive was built with old pairs at Ajmer workshop.
- 1899: Lady Curzon was first locomotive built in India, at Ajmer.
- January 26, 1950: Chittaranjan Locomotive Works (CLW) built first steam engine, Deshbandhu.
- 1952: Tata Engineering and Locomotive Company (TELCO) begins production of BG locomotives.
- 1961: CLW made the first 1500 DC electric locomotive Lokmanya
MADE EASY CIVIL ENGINEERING GATE NOTES : CLICK HERE
IMPORTANT FACTS REGARDING INDIAN RAILWAYS
- Biggest yard of India: Mugalsarai, Uttar Pradesh.
- Biggest railway crossing of India: Itarsi, Madhya Pradesh.
- Biggest railway station of India: Kharagpur.
- Longest railway River Bridge:Vembanad Rail Bridge, Kerala, 4.62 km.
- Railway station in maximum height: Ghum 2,258 m (7,407 ft) – Darjeeling, Himalayan Railway.
- First rail museum in India: New Delhi.
- First computerised railway reservation in India: New Delhi.
- First rail-bus service in India: Meratapur, Rajasthan.
- First rail minister of India: Asaf Ali.
- First women rail driver of India: Mumtaz Kathwala.
- Beginning of AC coaches in India: 1936
- First railway postal service in India: 1907.
- The longest distance train in India: Dibrugarh – Kanyakumari Vivek Express.
- Beginning of Insurance in railway: 1st April, 1994, with the name ‘Train passenger insurance scheme, by United India Insurance Company.
- Father of Indian Railway – Lord Dalhousie.
- Fastest train – The Bhopal Shatabdi Express,1988,between Agra and New Delhi.
- Slowest train in India- Nilgri Express, between Chennai and Mettupalayam
- First electric train – Deccan Queen, 1931, connects Mumbai with Pune.
- First double-decker train – Shatabdi train was flagged off in October 2011.
- First air-conditioned double-decker train – Shatabdi train from Mumbai to Goa.
- First underground railway (Metro Railway) – Kolkata Metro(1984).
- Largest Zone in Indian Railways – Northern Railway.
- A platform surrounded by rail lines from all the four sides – Island platform
- First railway station – Chhatrapati Shivaji Terminus railway station in Mumbai.
- Longest railway platform –Gorakhpur railway station, Uttar Pradesh.
- First broad gauge superfast train – Rajdhani express, New Delhi, Howrah 1st March, 1969.
- First metre gauge super fast train – pink city express New Delhi Jaipur 17th Oct, 1981.
- First narrow gauge super fast train – Shivalik Deluxe Express Kalka – Shimla 9th Aug, 1996.
- First time table 1853 Central India
- First stamp on Indian railways 4 annas 10th December, 1936 by King George.
- First automatic signalling system 1928
- First railway tunnel of Indian railway -Parsik tunnel.
- Division that has maximum number of tunnels – Kalka Simla division of Northern Railway (103 tunnels).
- Last railway station of Northern Railway and Indian Railway – Bajalta.
- Indian state has maximum rail routes – Uttar Pradesh, Himsagar Express passes through – 11 States(Jammu and Kashmir, Punjab, Haryana, Delhi, Uttar Pradesh, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh, Tamilnadu, Karnataka and Kerala).
- First female operator in Delhi Metro – Minakshi Sharma.
- First female to become the member of Railway Board – Vijaylaxmi Vishwanathan.
- Longest platform situated–Khadagpur (West Bengal).
- Train only for women run – From Churchgate to Boriwali in Mumbai.
- Metro Rail in Calcutta – 1984.
- Railway week celebrated on 10–16 April.
- 21 Railway Recruitment Boards are there in India.
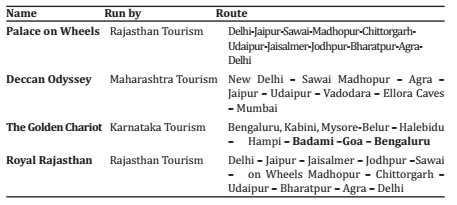
- First tourist rail – Palace on wheels in 1982 between Delhi–Jaipur.
- First monorail operate in India – From Sarhind to Alampur and Bhawani mandi to Patiala.
- India’s first indigenous steam engine – F–734.
- First telecommunication between guard and driver – Mumbai–New Delhi (Rajdhani Express).
- First Rajdhani Express ran between New Delhi–Howrah, 1969.
- First DC electrical rail engine – Lokmanya (CLW manufactured it in 1961).
- Southern Eastern Railway is known as ‘Blue chip’.
- Metroman – Shridharan (Ex. Delhi Metro Rail Engineer).
- First Duronto Express ran between Sialdah and New Delhi 18 September, 2009.
- First railway factory established in Jamalpur, 1890.
- Train runs between India and Pakistan – Samjhauta Express, Thar Express.
- Railway zone launched first Railway Time Table -Central Railway.
- State with minimum rail routes – Manipur.
- First blind friendly train, from Mysuru to Varanasi – Train no. 16226/ 16230.
GENERAL AWARENESS GUIDE FOR RRB JE CIVILENGGFORALL
DOWNLOAD LINK : CLICK HERE
PASSWORD : CivilEnggForAll
ACE ACADEMY GATE GENERAL ABILITY NOTES : CLICK HERE
OTHER USEFUL BOOKS
- BUILDING MATERIALS – MOCK TEST 1 (QUICK)
- TELANGANA STATE PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION – ASSISTANT ENGINEER 2023 – TSPSC AE 2023 CIVIL ENGINEERING EXAM SOLVED PAPER WITH EXPLANATIONS PDF FREE DOWNLOAD
- SSC JE 2023 CIVIL ENGINEERING (CPWD/CWC/MES) EXAM SOLVED PAPER PDF FREE DOWNLOAD
- BIHAR PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION ASSISTANT ENGINEER (BPSC AE) 2022 CIVIL ENGINEERING EXAM SOLVED PAPER WITH EXPLANATIONS PDF
- NHPC (NATIONAL HYDROELECTIC POWER CORPORATION) JUNIOR ENGINEER NHPC JE 2022 CIVIL ENGINEERING EXAM SOLVED PAPER PDF FREE DOWNLOAD

Leave a Reply