

Table of Contents
CONTENTS
PHYSICS
- MECHANICS
- PROPERTIES OF MATTER
- HEAT
- SOUND
- OPTICS
- ELECTRICITY
- MAGNETISM
- SEMICONDUCTOR ELECTRONICS
CHEMISTRY
- NATURE OF MATTER
- STRUCTURE OF ATOM
- CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS AND PERIODICITY IN PROPERTIES
- ACIDS, BASES AND SALTS
- METALS AND NON-METALS
- ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION
- GENERAL CONCEPTS OF CHEMISTRY
- SOME IMPORTANT MAN-MADE MATERIALS
- GENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
BIOLOGY
- DIVERSITY IN LIVING ORGANISMS
- CELLS AND TISSUES
- PLANT PHYSIOLOGY
- GENETICS AND EVOLUTION
- BIOLOGY IN HUMAL WELFARE
- DISEASES AND THEIR DEFENCE MECHANISM
- ECOLOGY AND ENVIRONMENTAL AWARENESS

MECHANICS
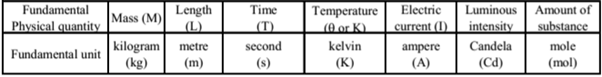
Physical Quantities : Those quantities which can describe the laws of physics and possible to measure are called physical quantities. The physical quantities which do not depend upon other physical quantities are called fundamental quantities. In Standard International (S.I.) system the fundamental quantities are mass, length, time, temperature, luminous intensity, electric current and amount of substance. The physical quantities which depend on fundamental quantities are called derived quantities e.g. speed, acceleration, force, etc.
Units : The unit of a physical quantity is the reference standard used to measure it.
IES MASTER CIVIL GATE STUDY MATERIALS : CLICK HERE
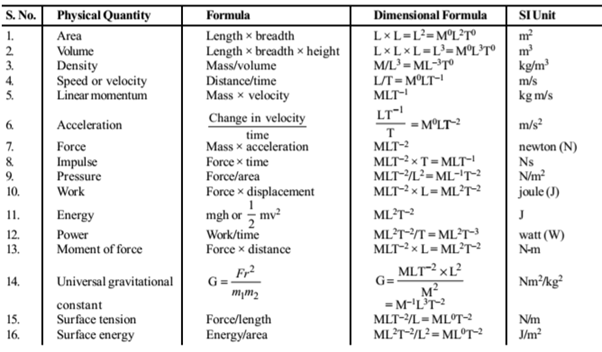
Derived Units : The units defined for the derived quantities are called derived units. e.g. unit of speed or velocity (metre per second), acceleration (metre per second2) etc.
Dimensions : The limit of a derived quantity in terms of necessary basic units is called dimensional formula and the raised powers on the basic units are dimensions.
HEAT
Temperature and Heat Temperature is defined as the degree of hotness or coldness of a body. It is a scalar quantity. Its S.I. unit is kelvin (K). Heat is a form of energy which causes sensation of hotness or coldness. The flow of heat is always from higher temperature to lower temperature. No heat flows from one body to other, when both the bodies are at the same temperature. The two bodies are said to be in thermal equilibrium. The SI unit of heat is joule. Its CGS unit is calorie, 1 cal = 4.2 joule
Measurement of Temperature : A branch of science which deals with the measurement of temperature of a substance is called thermometry. Thermometer is a device used to measure the temperature. Thermometer used for measuring very high temperatures are called pyrometer.
ACE CIVIL ENGINEERING GATE STUDY MATERIALS : CLICK HERE
OPTICS
Optics : The branch of physics which deals with the propagation, nature and behaviour of light is known as optics.
Light : Light is a form of energy which enables human beings and creatures to ‘see’ things. When light emitted from an object or reflected from the object enters our eyes we are able to see the object. We can’t see an object in dark even if we are in light because there is no light coming from the object to our eyes. Light is an electromagnetic radiation which exhibits properties like a wave as well as a particle. It always propagates in a straight line. Light travels with a speed nearly equal to 3 × 108 m/s. According to current theories, no material particle can travel at a speed greater than the speed of light.
Luminous and Non-luminous Objects : Luminous objects are those which emit its own light e.g., sun, glow-worm, burning candle, electric lights. Non-luminous objects do not give out its own light but are visible only when light from a luminous object falls on it. e.g., moon, earth, table, paper, etc. Transparent Translucent and Opaque materials Transparent materials are those which allow most of light to pass through them. Example: Glass, water, air. Translucent materials allow only a part of light to pass through it. We cannot see distinctly through them. Example: greased paper, paraffin wax, etc. Opaque materials do not allow any light to pass through it. They reflect or absorb all the light that falls on them. Example: Books, desk, stone, rubber, trees, etc.
MADE EASY CIVIL ENGINEERING GATE NOTES : CLICK HERE
NATURE OF MATTER
1. Substance (or chemical substance): A “substance” is a kind of matter that cannot be separated into other kinds of matter by any physical process. e.g. gold, silver, iron, sodium chloride, calcium carbonate etc.
2. Pure substance: is one that is a single substance and has a uniform composition. Such a substance always have the same texture and taste. e.g. water, salt, sugar etc.
3. Testing the purity of a substance: The purity of substance can easily be checked by checking its melting points in case of a solid substance or by checking its boiling points in case of a liquid substance.
4. Types of pure substances: Two different types of pure substances are (i) Element: An element is a substance which cannot be split up into two or more simpler substances by usual chemical methods of applying heat, light or electric energy. e. g. hydrogen, oxygen, sodium, chlorine etc. (ii) Compound: A compound is a substance made up of two or more elements chemically combined in a fixed ratio by weight e.g. H2O (water), NaCl (sodium chloride) etc.
5. Mixture: A mixture is a substance which consists of two or more elements or compounds not chemically combined together. e.g. Air is a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, inert gases, water vapour, carbon dioxide etc.
6. Types of mixtures: Mixtures are impure substances. They are of two types: (i) Homogeneous mixture: It has a uniform composition throughout and its components cannot be distinguished visually. e.g. a well mixed sample of vinegar. (ii) Heterogeneous mixture: It is one that is not uniform throughout. Different samples of a heterogeneous mixture may have different composition. e.g. a mixture of salt and pepper.
7. Solution: It is a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances whose composition can be varied. e.g. solution of common salt in water, solution of ammonia in water. Some other examples are lemonade, coke, pepsi etc.
8. Separating the components of a mixture: Various methods are used for separating the constituents of a mixture. Depending upon the type of mixture (i.e. whether it is a homogeneous mixture or heterogeneous mixture) different methods used are given below:

GENERAL SCIENCE GUIDE FOR RRB JE CIVILENGGFORALL
DOWNLOAD LINK : CLICK HERE
PASSWORD : CivilEnggForAll
ACE ACADEMY GATE GENERAL ABILITY NOTES : CLICK HERE
OTHER USEFUL BOOKS
- BUILDING MATERIALS – MOCK TEST 1 (QUICK)
- TELANGANA STATE PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION – ASSISTANT ENGINEER 2023 – TSPSC AE 2023 CIVIL ENGINEERING EXAM SOLVED PAPER WITH EXPLANATIONS PDF FREE DOWNLOAD
- SSC JE 2023 CIVIL ENGINEERING (CPWD/CWC/MES) EXAM SOLVED PAPER PDF FREE DOWNLOAD
- BIHAR PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION ASSISTANT ENGINEER (BPSC AE) 2022 CIVIL ENGINEERING EXAM SOLVED PAPER WITH EXPLANATIONS PDF
- NHPC (NATIONAL HYDROELECTIC POWER CORPORATION) JUNIOR ENGINEER NHPC JE 2022 CIVIL ENGINEERING EXAM SOLVED PAPER PDF FREE DOWNLOAD

Leave a Reply