

CONTENTS
- ROAD ENGINEERING
- CLASSIFICATION OF ROADS
- PLANNING SURVEYS
- PREPARATION OF PLANS
- HIGHWAY ENGINEERING
- HIGHWAY GEOMETRIC DESIGN
- HIGHWAY CONTROLS AND CRITERIA
- HIGHWAY CROSS SECTION ELEMENTS
- SIGHT DISTANCE
- DESIGN OF HORIZONTAL ALIGNMENT
- DESIGN OF VERTICAL ALIGNMENT
- TYPES OF PAVEMENT
- PAVEMENT MATERIALS
- TESTS FOR MEASURING THE STRENGTH PROPERTIES OF MATERIAL
- DESIGN OF RIGID PAVEMENTS
- WATER BOUND MACADAM ROADS
- HIGHWAY MAINTENANCE
- TRAFFIC ENGINEERING
- TRAFFIC CHARACTERISTICS
- TRAFFIC STUDIES
- INTERSECTIONS AND INTERCHANGES
- TRAFFIC SIGNS
- ALIGNMENT OF HILL ROADS
- ALIGNMENT SURVEY
- GEOMETRICS OF HILL ROADS
- DRAINAGE IN HILL ROADS
- MAINTENANCE PROBLEMS IN HILL ROADS

ROAD ENGINEERING
The road Pavements are generally constructed on small embankments, slightly above the general ground level wherever possible, in order to avoid the difficult drainage and maintenance problems. The term road or roadway thus constructed is therefore termed ‘highway’ and the science and technology dealing with road engineering is generally called ‘Highway Engineering’. In nutshell, it may be said that the highway engineering deals with various phase like development, planning, alignment, highway geometric design and location, highway traffic operation and its control, materials, Pavement design, construction and maintenance, economic considerations, finance and administration.
HIGHWAY ENGINEERING IES MASTER GATE STUDY MATERIAL PDF : CLICK HERE
CLASSIFICATION OF ROADS
The different types of roads are classified into two categories, depending on whether they can be used different seasons of the year.
- All weather roads and
- Fair weather roads
All weather roads are those which are negotiable during all. Weather, except at major river crossing where interruption to traffic is permissible up to a certain extent, the roads pavement should be negotiable during all weathers. Roads which are called fair weather roads; on there roads the traffic may be interrupted during monsoon season at causeways where streams may overflow across the roads.
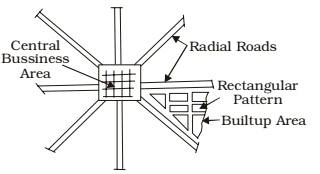
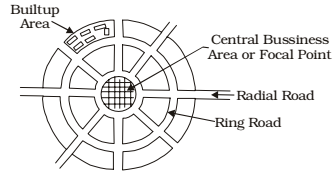
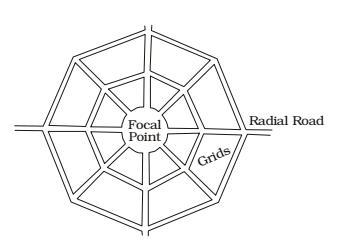
Road Patterns
The various road patterns may be classified as follows.
- Rectangular or block pattern
- Radial or star and block pattern
- Radial or star and circular pattern
- Radial or star and grid pattern
- Hexagonal pattern
- Minimum travel pattern
Each of these patterns have their advantages and limitations. There can be a number of other geometric pattern also. The choice of the pattern are very much depends upon the locality, the layout of different towns, villages, industrial and production centres and on the choice of the planning engineer.
PLANNING SURVEYS
Highway planning phase includes
- Assessment of road length requirement form area (it may be a district, state or the whole country).
- Preparation of master plan showing the phasing of plan in annual and or five year plans. Thus for caressing the road length requirements, field surveys are to be carried out to collect the data required for determining the length of the road system. The field surveys thus required for collecting the factual data may be called as planning surveys or factfinding surveys. The factual studies point to an intelligent approach for planning and there studies should be carried out if the high way programme is to be protected from inconsistent and short sighted policies.
TRANSPORTATION ENGINEERING ACE GATE STUDY MATERIAL PDF : CLICK HERE
The planning surveys consist of the following studies
- Economical studies: the various details to be collected are useful in estimating the economics involved in the highway development programme. Hence it is desirable to find the service give by each road system to the population and products of the area. All details of the existing facilities should be available before estimating the requirements such the economic justification can be made for each plan.
- Financial studies: The financial studies are essential to study the various financial aspects like sources of income and the manner in which funds for the project may be mobilized.
- Traffic or road use studies: All details of the existing traffic their volume and pattern of flow should be knows before any improvement could be planned. Traffic survey should be carried out in the whole area and on selected routes and locations in order to collect the different information regarding traffic.
- Engineering studies: All details of the topography, soil and other problems such as drainage, construction and maintenance problems should be investigated before a scientific plan or programme is suggested.
Surveys
- Topographic surveys.
- Soil surveys.
- Location and classification of existing roads
- Estimation of possible development in all aspects due to the proposed highway development
- Road life studies
- Traffic studies – Origin and Destination Studies
- Special problems in drainage, construction and maintenance of roads.
TRANSPORTATION ENGINEERING ACE GATE NOTES : CLICK HERE
HIGHWAY ENGINEERING
Transportation contributes to the economic, industrial, social and cultural development of any country. Transportation is vital for the economic development of any region since every commodity produced needs means of transportation at all stages from production to distribution.
HIGHWAY GEOMETRIC DESIGN
- Cross-section elements
- Sight distance consideration
- Horizontal alignment details
- Vertical alignment details
- Intersection details.
Under cross section elements, the consideration for the width of pavements formation and land, the surface characteristics and cross-slope of pavement are included. The sight distance or clear distance visible ahead of a driver at horizontal and vertical curves and at intersections governs the safe movements of vehicle. The change in read directions are made possible by introducing horizontal curves. Super-elevation is provided by raising the outer edge of pavement to counteract the centrifugal force developed on a vehicle traversing a horizontal curve, extra pavement width is also provided on horizontal curves.
DESIGN CONTROLS AND CRITERIA
The geometric design of highways depends on several design factors. The important of these factors which control the geometric elements are
- Designed speed
- Topography
- Traffic factors
- Designed hourly volume and capacity
- Environment and other factors.
TRANSPORTATION ENGINEERING MADE EASY GATE NOTES PDF : CLICK HERE
HIGHWAY CROSS SECTION ELEMENTS:-
- Pavement surface characteristics: The pavement surface depends on the pavement type which is decided based on the availability of material and funds, volume and composition of traffic subgrade and climatic conditions, construction facilities and consideration. The important surface characteristics of the pavement are the friction unevenness, light reflecting characteristics and drainage of surface water.
- Friction: When a vehicle negotiates a horizontal curve, the lateral friction developed counteracts the centrifugal force. Thus, It governs the safe operating speed. Frictional force is an important factor in the acceleration and retardation abilities of vehicle. The maximum coefficient of friction comes into play only when the braking efficiency is high enough to partially arrest the rotation of the wheels on application of brakes at low speed. Skid occurs when the side without revolving or when wheels partially revolve ,i.e when the path, travelled along the road surface is more than the circumferential movements of the wheel due to rotation.
- Pavement unevenness: Higher operating speed are possible on even pavement surfaces with less undulations than on uneven and poor surfaces, pavement surface should hence be maintained with minimum possible unevenness such that the desired speed can be maintained in conformity with other geometric standards.
- Light reflecting characteristics: Night visibility very much depends upon the light reflecting characteristics of pavement surface. The glare caused by the reflection of headlights is considerably high on wet pavement surface than on the dry pavement.
HIGHWAY ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIAL FOR RRB JE PDF CIVILENGGFORALL
DOWNLOAD LINK : CLICK HERE
PASSWORD : CivilEnggForAll
OTHER USEFUL BOOKS
- BUILDING MATERIALS – MOCK TEST 1 (QUICK)
- TELANGANA STATE PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION – ASSISTANT ENGINEER 2023 – TSPSC AE 2023 CIVIL ENGINEERING EXAM SOLVED PAPER WITH EXPLANATIONS PDF FREE DOWNLOAD
- SSC JE 2023 CIVIL ENGINEERING (CPWD/CWC/MES) EXAM SOLVED PAPER PDF FREE DOWNLOAD
- BIHAR PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION ASSISTANT ENGINEER (BPSC AE) 2022 CIVIL ENGINEERING EXAM SOLVED PAPER WITH EXPLANATIONS PDF
- NHPC (NATIONAL HYDROELECTIC POWER CORPORATION) JUNIOR ENGINEER NHPC JE 2022 CIVIL ENGINEERING EXAM SOLVED PAPER PDF FREE DOWNLOAD

Leave a Reply