
Table of Contents
TRANSPORTATION ENGINEERING PART-2
RAILWAY ENGINEERING (LATEST NOTES)
MADE EASY GATE HANDWRITTEN CLASSROOM NOTES
FREE DOWNLOAD PDF
Railway Engineering Made Easy GATE Handwritten Notes Download PDF for Free only at CivilEnggForAll
Railway Engineering Made Easy GATE Handwritten Notes Download PDF
PLEASE NOTE : WE PROVIDE ONLY VERIFIED NOTES AND MATERIALS. ALL THE OTHER NOTES WHICH ARE AVAILABLE IN THE INTERNET WITH THE NAME MADE EASY CIVIL NOTES ARE FAKE AND ARE NORMAL CLASSROOM NOTES OF SOME COLLEGE. WE ALWAYS TRY TO BRING OUT QUALITY NOTES FOR FREE AND FOR THE SAKE OF STUDENTS WHO ARE REALLY WORKING HARD DAY AND NIGHT AIMING GOOD GATE/IES RANKS.
Important Components of Railway track :
1. Formation
2. Ballasts
3. Sleeper
4. Fixtures
5. Rails
Gauge : Distance between inner forces of two rails (Running face)
Running face is the face on which wheel will be there.
Broad Gauge : 1.676m
Meter Gauge : 1m
Narrow Gauge : 0.762m
Lighter Gauge : 0.610m
Standard Gauge : 1.435m

Coning of Wheels :
The wheels are made cone shaped having different diameters at different cross sections. Diameter near flange is more than the diameter near other ends. The rails are also laid at a slope of lin20 (same slope of wheel face) This is called coning of wheels.
Purpose of Coning :
1. On a straight track : To keep the wheel assembly in central position to avoid derailment.
2. To reduce wear and tear of centrifugal force the wheen assembly in move in outward direction, so diameter on outer rail will increase. So the distance travelled on outer rail will become more as required. Due to difference of diameter on two rails, the trains will be moving on a circular track and distance travelled on two tracks will be adjusted as required.
Only some part of difference is adjusted due to coning. Remaining part is covered by slip or skid on the surface.
Due to cone shaped wheels, diameter of wheel is not same at each section.
On straight track, the wheel will always move in central position in such a way that diameter at contact point with rail is same on the two rails. If the train or axle of wheel try to move in any direction, diameter of wheel on one rail will increase. So the axle will start moving on a circular track. Thus the wheel assembly will be automatically returned back in its central position.
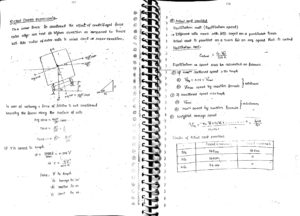
On a curved track : The distance on the rails are partially adjusted due to centrifugal force due to which the train moves in outward direction, due to which diameter on outer rail becomes more than inner rails.
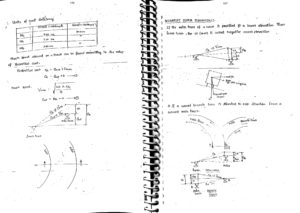
Long Welded Rails :
The rails are made of a particular length (for Broad gauge track, maximum length of 12.8m is used) The joints to be provided in the railway tracks are one of the weakest locations. To avoid joints, rails are welded together. Long welded rails are used where all the rails are welded for a long length. The stress caused due to difference in temperature are arrested by the fixtures and rails are not allowed to move. So no expansion joints are required. A minimum length is required to avoid the movement of rail due to temperature variation.
DOWNLOAD LINK : Railway Engineering Made Easy GATE Handwritten Notes Free Download PDF
PASSWORD : CivilEnggForAll
DOWNLOAD HIGHWAY ENGINEERING NOTES : CLICK HERE
OTHER USEFUL LINKS FROM CIVILENGGFORALL
HIGHWAY ENGINEERING MADE EASY GATE HANDWRITTEN NOTES : CLICK HERE
SURVEYING AE & AEE HANDWRITTEN NOTES : CLICK HERE
GENERAL SCIENCE AE AEE HANDWRITTEN NOTES : CLICK HERE
STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS AE & AEE HANDWRITTEN NOTES : CLICK HERE
PERT AND CPM AE AEE HANDWRITTEN NOTES PDF : CLICK HERE
Geography AE AEE Ace Academy Handwritten Notes PDF : CLICK HERE TO DOWNLOAD
Indian Polity AE AEE Civil Engineering Handwritten Notes PDF : CLICK HERE TO DOWNLOAD
Economics AE AEE Civil Engineering Handwritten Notes PDF : CLICK HERE TO DOWNLOAD

Leave a Reply