
STRENGTH OF MATERIALS
ASSISTANT ENGINEER & ASSISTANT EXECUTIVE ENGINEER
HANDWRITTEN NOTES
ACE ACADEMY TRAINING NOTES
FREE DOWNLOAD PDF
Strength of Materials AE & AEE Ace Academy Handwritten Notes PDF Free Download. Only Google Drive download links. No hidden ads.

Assistant Executive Engineer (AEE) and Assistant Engineer (AE) are the government posts where Civil Engineers will be recruited in different departments like Irrigation, Rural, Roads, CAD, Ground Water, Tribal Welfare and more. There is a heavy competition for getting the AE and AEE government jobs in different states. ACE Academy is giving one of the top most quality in AE and AEE Government Exams coaching.
Download Transportation Engineering AE and AEE ACE Academy Handwritten Notes at CivilEnggForAll
The main aim of strength of materials is to access various properties of materials and use them according to the requirement.
Strength : Ability of a material to resist external load against failure.
Note :
The primary design parameter is strength.
All the designs of engineering are strength based design only.
Stiffness : Ability to resist deformation is stiffness. Stiffness is the secondary design parameter.
Increase in deflection will decreases the stiffness and increases the flexible.
Assumptions :
1. Material is solid and continuous. No cracks in the material and no voids in the material.
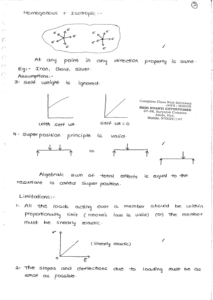
2. Material are homogeneous and Isotropic.
All the base materials without any mixture is called Homogeneous.
Note : Wood is a homogeneous but not Isotropic. Brass is a Isotropic but not homogeneous.

All homogeneous material need not be isotropic and vice versa but few homogeneous materials are also Isotropic.
Ortho = Perpendicular
Tropic = Direction Point
At one point in perpendicular direction but properties are different.
Example : Layered material are orthotropic like wood, coal, mica, asbestos.
Anisotropic (or) Aleotropic (or) Non Isotropic : At any one point in different direction properties are different. Example : Materials with voids and cracks.
Homogeneous + Isotropic : At any points in any direction property is same.
Example : Iron, Gold, Silver
Limitations :
1. All the loads acting over a member should be within proportionality limit. The members must be linearly elastic.
2. The slopes and deflections due to loading must be as small as possible.
3. Super position principle is not valid for impact load, strain energies, deep beams. In case of deep beams due to loading torsion develops which makes distortion in the shape. Therefore the principle is not valid.
4. Circular shaft subjected to torsion super position is valid, non circular shaft with torsion the principle is not valid.
5. Long columns, sinking of supports, this principle is not valid.
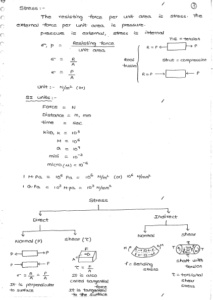
Elasticity : A material which regains its orginal size and shape on removal of load.
Plasticity : A material undergoes permanent deformation at constant loading is plasticity.
Ductility : The property by which the material can be made into thin wire.
Ductility is related to tension. It is strong in tension and weak in shear, moderate in compression.
Malleability : The property by which the material is made into thin sheets. It is related to compression by pressing or rolling.
Brittle : It fails suddenly such a material is called as Brittle. Brittle materials are strong in compression, moderate in shear, weak in tension.
Toughness : Resistance of a material against sudden or impact loading.
Fatigue : Reduction of a material due to repeated loading is fatigue
DOWNLOAD LINK : Strength of Materials AE & AEE Ace Academy Handwritten Notes PDF : CLICK HERE TO DOWNLOAD
DOWNLOAD SURVEYING AE & AEE HANDWRITTEN NOTES : CLICK HERE
DOWNLOAD FLUID MECHANICS AE & AEE HANDWRITTEN NOTES : CLICK HERE
DOWNLOAD STRENGTH OF MATERIALS AE & AEE HANDWRITTEN NOTES : CLICK HERE
TSPSC AEE/AE SYLLABUS
Paper-I: GENERAL STUDIES AND GENERAL ABILITIES
1. Current affairs – Regional, National and International.
2. International Affairs.
3. General Science; India’s Achievements in Science and Technology.
4. Environmental issues; Disaster Management- Prevention and Mitigation Strategies.
5. Economic and Social Development of India and Telangana.
6. Physical, Social and Economic Geography of India.
7. Physical, Social and Economic Geography and Demography of Telangana.
8. Socio-economic, Political and Cultural History of Modern India with special emphasis on
Indian National Movement.
9. Socio-economic, Political and Cultural History of Telangana with special emphasis on
Telangana Statehood Movement and formation of Telangana state.
10. Indian Constitution; Indian Political System; Governance and Public Policy.
11. Social Exclusion; Rights issues such as Gender, Caste, Tribe, Disability etc. and
inclusive policies.
12. Society, Culture, Heritage, Literature of Telangana.
13. Policies of Telangana State.
14. Logical Reasoning; Analytical Ability and Data Interpretation.
15. Basic English. (10th class Standard)
PAPER-II: CIVIL ENGINEERING (DEGREE LEVEL)
1. Building Materials And Construction: Bricks–
Types of Bricks, Indian standard classification, properties; Stones – Types of stones, classification, properties, dressing and polishing of stones; Methods of Quarrying; Cement – Different grades and types of cement, properties and IS specifications; Aggregates – coarse and fine aggregate, properties and IS specifications; Cement Mortar – Proportions of cement mortar for various applications; Concrete – Constituents of Concrete, Different grades of Concrete, mix proportioning using IS Code, Properties of fresh and hardened Concrete; Admixtures – Types of Admixtures
2. Strength of Materials And Theory of Structures: Strength of Materials: Simple stresses and strains, elastic constants and relationship between them; Compound bars; Temperature stresses; Shear forces and bending moment diagrams for beams; Principal stresses and Mohr’s circle of stress, Theory of bending and bending stresses ; Shear stress distribution; Theory of torsion; Springs; Deflections of beams; Thin and thick cylinders;; Analysis of trusses, Betti-Maxwell theorem; Shear centre and unsymmetrical bending. Theory of Structures: Direct and bending stresses; Columns and struts; Strain energy method; Moving loads and influence lines; Arches and suspension bridges; Static and kinematic indeterminacy; Moment distribution, Slope deflection, and Kani’s methods applied to continuous beams and portal frames; Column analogy and matrix methods of analysis.
3. RCC and Steel Structures: Concrete Structures: Materials, permissible stresses and IS Specifications; Working stress methods; Limit State Method – Stress Blocks parameters, design of Beams, Slabs, Columns and Footing; Design for Shear and Torsion; Design of Retaining Walls, Water tanks, and T-Beam Slab bridges; Yield line theory. Steel Structures: Properties of steel sections, permissible stresses, IS Specifications; Riveted and welded joints and connections; Design of simple and compound Beams and Columns, Column bases, Roof trusses, Plate and Gantry Girders; Plate Girder Lattice Girder Railway bridges, and Bearings. Plastic analysis.
Pre-Stressed Concrete: Basic concepts, material for pre-stressing, losses in Pre-stress, classification of pre-stressing system; Analysis of PSC Sections.
4. Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulics: Fluid Properties :
Measurement of Pressure – Manometers; Fluid Kinematics – Classification of Fluids, Stream function and Velocity potential, significance and use of Flownets, Fluid dynamics – Continuity equation, Bernoulli’s equations and Impulse momentum equation; Laminar and Turbulent flow through pipes – significance of Reynolds number, Hagen – Poiseuille’s equation, Darcy – Weisbach equation, Friction factor, Water hammer phenomenon; Compressible flow – Bernoulli’s equation for Isothermal and Adiabatic conditions, Mach Number, Mach cone, stagnation properties; Steady uniform flow through open channels; Gradually varied flows – significance of Froude number, classification and computation of Flow profiles, Hydraulic jump, Surges; Boundary layer – Laminar and Turbulent Boundary layer, Boundary layer thickness, rough and smooth Boundaries, Boundary layer separation; Dimensional analysis and similarity laws; Hydraulic Turbines – classification, Velocity triangles, principles and design of reaction and impulse turbines; Centrifugal pumps – specific speed, work done and efficiency, characteristic curves.
5. Hydrology and Water Resources Engineering:
Hydrological cycle; Rainfall – types and measurement, network design; Infiltration – Ф- index; Runoff – process, factors and determination of runoff, dependable yield; Floods –flood hydrograph, computation of flood peak using rational formula, unit hydrograph method and Gumbel’s extreme value methods; Groundwater – types of aquifer and properties, Darcy’s law, specific yield, steady radial flow to wells in confined and unconfined aquifers; Irrigation – types and advantages, soil water plant relationship, consumptive use, duty, delta, base period, crops and their water requirements; Single and multipurpose projects; Dams – classification, forces and design of Gravity dam and Earth dam; Spillways – types, energy dissipation, stilling basin, Appurtenances; Canals – alignment, Kennedy’s and Lacey’s theories, lining of Canals; Weirs – components, design of vertical drop and sloping glacis weir; Seepage forces – Bligh’s Theory, Khosla’s theory; Canal falls – types and design principles; Cross drainage works – classification and design principles of aqueducts; Hydropower – classification and principle components of Hydroelectric power plants.
6. Environmental Engineering: Water supply – objectives, rate of demand, population forecasts; Analysis of water – classification, design of coagulation, sedimentation, filtration, disinfection and softening processes; Methods of layout of distribution pipes – Hardy cross method; Waste water engineering – systems of sewerage, hydraulic formulae and design of sewers, BOD, COD, self purification of natural streams, methods of sewage disposal; Treatment of sewage – principles and design of grit chamber, sedimentation tanks, trickling filters, activated sludge process, sludge digestion tanks, septic tanks; Municipal solid waste – characteristics, collection and transportation of solid wastes; Air Pollution – types and sources of pollutants, air quality standards; Noise pollution – Impacts and permissible limits, measurement and control of noise pollution.
7. Transportation Engineering: Highway Classification as per IRC; Highway alignment; Engineering Surveys; Geometric Design; Cross sectional elements of road; Gradient; Grade compensation; Traffic Surveys – speed, Volumes, origin and destination; Highway capacity and level of service as per HCM 2000; Intersection – at grade and grade separated; Channelization; Rotary intersection; signal design – webstar method, traffic signs, pavement marking; Parking studies, accidental studies, pavement types, Factors considered for pavement design, flexible and rigid pavements design concepts. Railway Engineering: Permanent way, rails, sleepers, ballast; Creep, coning of wheel, rail fixtures and fastenings, super elevation, cant deficiency, curves, turnout; Points and crossings. Airport Engineering: Selection of site of Airport, runway orientation and design, wind rose diagram, basic run way length, correction to basic runway length.
8. Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering: Soil Mechanics: Physical properties of soils, Classification and identification, Permeability, Capillarity, Seepage, Compaction, Consolidation, Shear Strength, Earth pressure, Slope stability; Foundation Engineering: Site investigations, stress distribution in soils, Bearing capacity, Settlement analysis, Types of Foundation, Pile foundations, Foundations on expansive soils; swelling and its preventions; Coffer dams, Caissons, Dewatering, Bracing for excavations, Newmark charts, machine foundations.
Engineering Geology: Mineralogy, Structural Geology, Groundwater Exploration methods; Engineering Geology applications for Tunnels, Dams and Reservoirs; Geological hazards and preventive measures.
9. Estimation, Costing and Construction Management: Abstract estimate: Detailed estimate – centerline, long & short wall method, various items of Civil Engineering works as per Indian Standard, General Specifications – Earth Work, Brick / Stone Masonry in Cement Mortar, RCC, Plastering in Cement Mortar, Floor finishes, white wash, colour wash; Standard schedule of rates, lead and lift, preparation of lead statement; Computation of earth work – Mid-ordinate, Mean Sectional area, Trepezoidal method, Prismoidal Rule; Approximate estimate – Plinth area and cubic rate estimate.
10. Surveying: Principle and classification of surveying, chain surveying; Compass surveying; Levelling and contouring; Theodolite surveying; curves; Introduction and Fundamental concepts of electronic measuring instruments – EDM, Total station, GIS & GPS.

Leave a Reply