

CONTENTS
- Basic Principles
- Maps
- Representative Fraction (R.F.)
- Errors
- Classification of Survey
- Chain Survey
- Compass Survey
- Theodolite Survey
- Tachometric Survey
- Plane Table Survey
- Triangulation Survey
- Photogrammetry

What is Surveying?
Surveying is the science of determining relative positions of objects on the surface of the earth by taking measurements of distances, directions and elevations.
Basic Principles of Surveying
- Locating a point on the surface of the earth by atleast two reference points.
- “Working from whole to the part”. In this system first a system of control points are fixed with great precision. Minor control points are then established with less precision and details are located afterwards.
Types of Surveying
- Plane Surveying – In this survey effect of curvature of the earth is neglected assuming earth’s surface to be plane. Generally areas less than 260 sq.km.(100 sq miles) are treated as plane. For engineering works, this type of survey is generally followed.
- Geodetic or Trigonometrical Surveying – In this survey curvature of the earth is taken into account.
- Map – The representation of the earth surface on a small scale, is called a map and it is called plan of the scale is large.
- Scale – Fixed ratio that a distance on map bears with the corresponding distance on the ground is called scale. e.g. 1 cm = 10 m.
- Reconnaissance – It is the preliminary inspection of the area undertaken before survey work of that area is planned.
IES MASTER CIVIL ENGINEERING GATE STUDY MATERIALS PDF: DOWNLOAD LINK
ACE ACADEMY CIVIL ENGINEERING GATE STUDY MATERIALS PDF: DOWNLOAD LINK
CLASSIFICATI ON OF SURVEY
- Chain survey
- Compass survey
- Theodolite survey
- Tachometric survey
- Plane table survey
- Triangulation survey
- Aerial survey
- Photogrammetric survey
CHAIN SURVEY
In this method of surveying, the area is divided into a network of triangles and sides of the various triangles are measured directly in the field with chain or tape and no angular measurements are taken. It is most suitable when area to be surveyed is small in extent and is fairly level and open with simple details.
- Station: End points of a chain line are called stations and the station on beginning or end of main chain line is called main survey station. Tie stations are selected anywhere on the chain line. They are at the beginning or end of a tie or subsidiary line.
- Base line: Longest line of the main survey lines is designated as base line.
- Tie line: It connects tie stations or subsidiary stations on the main survey lines and is provided primarily with the object to facilitate taking offsets to objects distant from the main lines. It also serves as a check line.
- Well conditioned Triangle: It is a well shaped triangle should not have angles less than 30o or more than 120o
Instruments Used in Chain Survey
- Chain – Following types of chains are used
- Metric chain: It is available in lengths of 5, 10, 20 and 30 meters.
- Gunters chain: It is available in 66 ft length, provided with 100 links
- Engineer’s chain: It is 100 ft long with 100 links
- Revenue chain: It is 33 ft long, provided with 16 links.
- Arrows
- Pegs
- Ranging rods
- Offset rods
- Plasterer’s lathes and whitest
- Plumb bob.
Ranging a Line – It is a process of marking number of intermediate points on survey line joining two stations in the field so that length between them may be measured correctly.
Methods of Ranging
- Direct Ranging: In this method, raging rods are placed along the chain line, by direct observations from either end station.
- Indirect Ranging: When end stations are not intervisible, then intermediate ranging rods are placed in line either by reciprocal ranging or by running a random line, or by geometric interpolation by constructing rectangle or suitable triangles
Setting out Right Angles
Following instruments used in setting out right angles
- Cross staff
- French cross staff
- Adjustable cross staff
- Optical square
- Prism square.
Planimeter – It is used for measuring area of a given figure. For reducing and enlarging the areas, pentagraph is used. Sometimes proportional compass is also used.
Selection of Survey Stations
Following points are considered in selection of a survey station
- Survey stations must be mutually intervisible.
- Survey lines should be as few as practicable and such that the framework can be plotted easily.
- A long base line should run (preferably on level ground) through middle of the area to provide a back bone to hang the triangles.
- Main survey lines should run through as level ground as possible.
- Well conditioned triangles should be formed by the main lines.
- Each triangle should be provided with a check line.
- Survey lines should be such that details can be located by short offsets (offset length must not exceed the limiting length of offset).
- To the extent practicable, the main survey lines should not pass through obstacles.
Offset
It is the lateral distance of an object or ground feature measured from a survey line. Types of Offsets. There are two types of offsets
- Perpendicular offset. It comprises of following
- Perpendicular distance from the object to nearest chain line
- Chainage of the foot of the perpendicular (from object to the chain line) from starting end of the chain line.
- Oblique offset Position of an object P can also be determined by measuring its distances from two known points A and B on the nearest chain line. Two distances PA and PB (called oblique offset lengths) are measured and the chainages of A and B (from starting end of the chain line) are noted. Oblique offsets fix a point more accurately than perpendicular offsets.
COMPASS SURVEY
The branch of surveying in which directions of survey lines are determined by a compass and their lengths by chain or tape directly on the surface of the earth, is called compass surveying. Before recommending compass survey for any area, it must be ascertained that area is not magnetically disturbed.
ACE ACADEMY CIVIL ENGINEERING GATE HANDWRITTEN CLASSROOM NOTES PDF: DOWNLOAD LINK
MADE EASY CIVIL ENGINEERING GATE HANDWRITTEN CLASSROOM NOTES PDF: DOWNLOAD LINK
Traverse
A series of connected straight lines each joining two points on the ground, is called a traverse. End points are called traverse stations and straight lines between two consecutive stations, are called traverse legs.
Closed Traverse
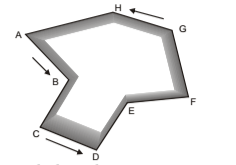
Traverse which either originates from a station and returns to the same station completing a circuit, is called closed traverse
Open Traverse
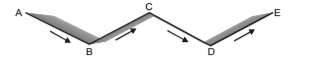
The traverse which neither returns to its starting station nor closes on any other known station, is called an open traverse.
Classification of Traverses (Based on Instruments used)
- Chain Traversing or Chain Angles Method: In chain traversing, entire work is done by a chain or tape and no angle measuring instrument is needed. Angle computed by the measurements, is called chain angle.
- Compass Traversing: Traverse in which angular measurements are made with a surveying compass, is called compass traversing. Traverse angle between two consecutive legs is computed by observing magnetic bearing of the sides.
- Plane Table Traversing: Traverse in which angular measurements between traverse sides are plotted graphically on a plane table with the help of an alidade, is called plane table traversing.
- Theodolite Traversing: Traverse in which angular measurements between traverse sides are made with a theodolite, is called theodolite traversing.
- Tachometric Traversing: Traverse in which direct measurements of traverse sides by chaining is dispensed and these are obtained by making observation with a tachometer, is called tachometric traversing.
SURVEYING TEXTBOOKS PDF: CLICK HERE
SURVEYING MADE EASY GATE NOTES PDF: CLICK HERE
SURVEYING ACE ACADEMY GATE NOTES PDF: CLICK HERE
Parts of surveying compass
- Magnetic needle
- Graduated ring
- Sighting vanes
- Reading system
- Tripod
Types of surveying compass
The compasses are of two types. Following three types of compasses are commonly used:
- Prismatic compass
- Surveyor ‘s compass
- Transit compass.
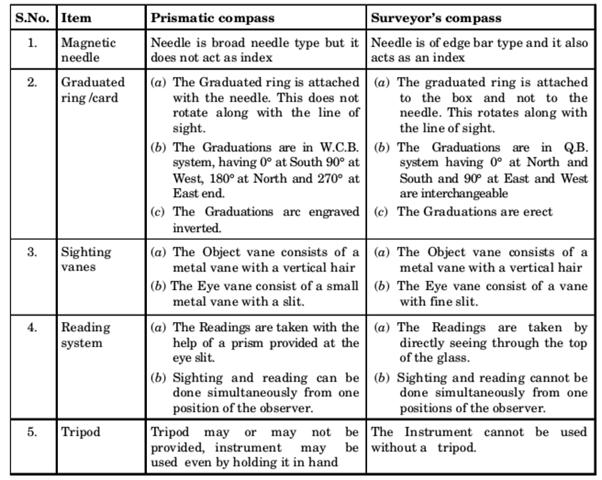
Comparison between Surveyor’s Compass and Prismatic Compass
Meridian
- True meridian: Meridian of a place is the direction indicated by an imaginary plane passing through that place and the two (north and south) geographical poles. The horizontal angle between a line and the true meridian is called true bearing of the line. It is also called azimuth.
- Magnetic meridian: The direction indicated by a freely suspended and properly balanced magnetic needle unaffected by local attractive force is called magnetic meridian. The horizontal angle which a line makes with this meridian is called magnetic bearing or simply bearing of the line.
- Arbitrary meridian: For small surveys any convenient direction may be taken as a meridian
Bearing
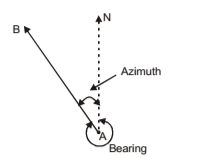
The horizontal angle between and reference meridian and the survey line measured in a clockwise direction, is called bearing. Reference direction may be any of the following:
- True Bearing – The horizontal angle between true meridian and the survey line measured in a clockwise direction, is called true bearing of the line. It is a constant quantity.
- Azimuth – The smaller angle which a survey line makes with the true meridian, is called azimuth.
- Magnetic Bearing – Horizontal angle which a line makes with the magnetic meridian, is called magnetic bearing. It is not constant at a point but varies with laps of time.
SURVEYING PART-1 CIVIL ENGINEERING GATE 2020 STUDY MATERIAL FREE DOWNLOAD PDF
DOWNLOAD LINK : CLICK HERE
PASSWORD : CivilEnggForAll
OTHER USEFUL BOOKS
- CIVIL ENGINEERING TEXTBOOKS WITH DOWNLOAD LINKS
- IES MASTER CIVIL ENGINEERING GATE STUDY MATERIALS PDF
- ACE ACADEMY CIVIL ENGINEERING GATE STUDY MATERIALS PDF
- BUILDING MATERIALS – MOCK TEST 1 (QUICK)
- TELANGANA STATE PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION – ASSISTANT ENGINEER 2023 – TSPSC AE 2023 CIVIL ENGINEERING EXAM SOLVED PAPER WITH EXPLANATIONS PDF FREE DOWNLOAD
- SSC JE 2023 CIVIL ENGINEERING (CPWD/CWC/MES) EXAM SOLVED PAPER PDF FREE DOWNLOAD
- BIHAR PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION ASSISTANT ENGINEER (BPSC AE) 2022 CIVIL ENGINEERING EXAM SOLVED PAPER WITH EXPLANATIONS PDF
- NHPC (NATIONAL HYDROELECTIC POWER CORPORATION) JUNIOR ENGINEER NHPC JE 2022 CIVIL ENGINEERING EXAM SOLVED PAPER PDF FREE DOWNLOAD

Leave a Reply