

CONTENTS
- SIMPLE STRESS
- STRESS AND STRAIN IN TWO DIMENSIONS
- MOHR’S CIRCLE
- ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM SHEARING STRESS
- TRANSFORMATION OF STRAIN COMPONENTS
- RELATION BETWEEN ELASTIC CONSTANTS
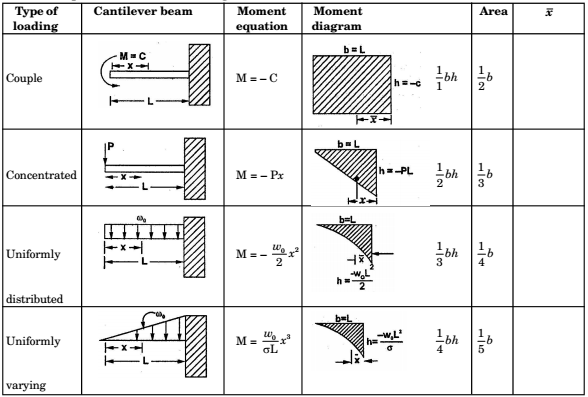
- BENDING MOMENTS AND SHEAR FORCE
- BEAM DEFLECTIONS
- COLUMNS
- THEORIES OF FAILURE
- TORSION

SIMPLE STRESS
- Strength of materials deals with the relations between externally applied loads and their effects on bodies.
- If the x-axis is normal to the section, the section is known as the x-surface or, more briefly, the x face.
- The first subscript denotes the face on which the component acts; the second subscript indicates the direction of the particular component thus P is the force on the x face acting in the y direction.
- The purpose of studying strength of materials is to ensure that the structures used will be safe against the maximum internal effects that may be produced by any combination of loading
- Density of steel = 7850 kg/m3
- Young’s modulus of elasticity of steel = 200 GPa = 2 x 105 MPa
- Rigidity modulus (G) = 80 GPa = 0.8 x 105MPa
- Stress, σ = P/A or dP/dA
- One pascal = 1 N/m2
- PSI = Pound/inch2
- KIP = Kilo Pound
- KSI = 1000 pond/inch PSf = Pond/ft2
- The condition under which the stress is constant or uniform is known as simple stress.
STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS IES MASTER GATE STUDY MATERIAL PDF: CLICK HERE
Shearing stress or Tangential stress
Shearing stress is caused by force acting along or parallel to the area resisting the forces. The shear occurs over an area parallel to the applied load. This called direct shear in contrast to the induced shear.
A uniform shearing stress will exist when the resultant shearing force V passes through the centroid of the cross section being sheared.
τ = V/A
Bearing Stress
Bearing stress differs from compressive stress in that the compress stress is the internal stress caused by a compressive force, whereas the bearing stress is a contact pressure between separate b….
The result of an excessive bearing stress is to cause yielding of the plate or the rivet or both.
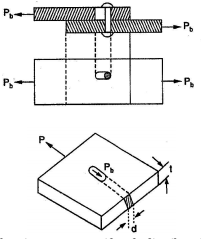
STRESS AND STRAIN IN TWO DIMENSIONS
Stress at a Point
The average stress over an area is obtained by dividing the force by the area over which it acts. If the average stress is constant over the area, the stress is said to be uniform. If the stress is not uniform, then stress at a point is determined. So, stress at a point defines the uniform stress distributed over a differential area (or permitting the area enclosing the point to approach zero as a limit).
Variation of Stress with Inclination of Element: Magnitude and type of stress depend on the inclination of an element.
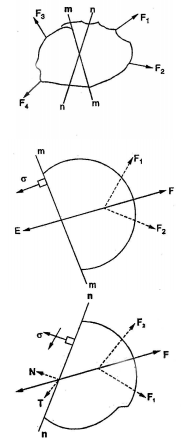
There are two sections m-m and n-n passing through the body on which several forces acts. Section m-m is perpendicular to the resultant F of F1 and F2 and section n-n is inclined to F. Thus, element in Fig. (b) is subjected only to a normal stress while element in above figure is subjected to both normal and shearing stresses.
Note: Thus, at same position in a stressed body, the stresses on an element vary with the orientation of the element.
STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS ACE GATE STUDY MATERIAL PDF: CLICK HERE
COLUMNS
A column is a compression member that under gradually increasing loads it fails by buckling at loads considerably less than those required to cause failure by crushing. A compression member is generally considered to be a column when its unsupported length is more than 10 times its lateral dimension. Long column fails by buckling, intermediate by a combination of crushing and buckling, short compression blocks by crushing.
Note: An ideal column is homogenous that is initially straight and is subjected to axial compressive loads. However, actual columns have small imperfections of material and fabrication as well as unavoidable accidental eccentricities of load. The initial crookedness of the column, together with the placement of the load, causes an intermediate eccentricity, e with respect to the centroid of a, typical section.
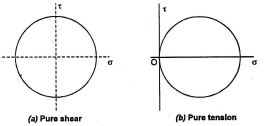
THEORIES OF FAILURE
Various theories of failure have been proposed, their purpose being to establish from the behaviour of a material subjected to simple tension or compression tests, the point at which failure will occur under any type of combined loading. By failure we mean either yielding or actual rupture, whichever occurs first.
The Maximum Stress Theory
The maximum stress theory was proposed by Rankine. It states that failure occurs when the maximum principal stress on an element reaches a limiting value, the limit being the yield point in a simple tension test (or ultimate strength, if the material is brittle). Mohr’s circles for the pure shear and pure tension in parts (a) and (b)
The Maximum Strain Theory
According to the maximum strain theory, a ductile material begins to yield when the maximum principal strain reaches the strain at which yielding occurs in simple tension or when the minimum principal strain equals the yield point strain in simple compression.
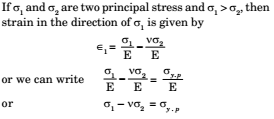
The Maximum Shear Stress Theory
It is called Guest theory. According to this theory yielding begins when the maximum shearing stress equals the maximum shearing stress developed at yielding in simple tension.
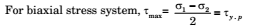
STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS MADE EASY GATE NOTES PDF: CLICK HERE
The Mises Yield Theory
This theory is also known as the maximum shear distortion theory. According to this theory, yielding can occur in a general three dimensional state of stress when the root mean square of the differences between the principal stresses in equal to the same value in a tensile test.
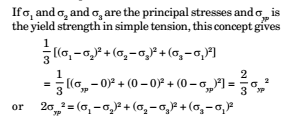
Note: Out of these theories, experimental work shows best agreement with the Mises yield theory when applied to ductile materials. For rupture in brittle materials, such as cast iron, the maximum stress theory is generally prepared.
THEORY OF STRUCTURES STUDY MATERIAL FOR SSC JE PDF CIVILENGGFORALL
DOWNLOAD LINK : CLICK HERE
PASSWORD : CivilEnggForAll
OTHER USEFUL BOOKS
- BUILDING MATERIALS – MOCK TEST 1 (QUICK)
- TELANGANA STATE PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION – ASSISTANT ENGINEER 2023 – TSPSC AE 2023 CIVIL ENGINEERING EXAM SOLVED PAPER WITH EXPLANATIONS PDF FREE DOWNLOAD
- SSC JE 2023 CIVIL ENGINEERING (CPWD/CWC/MES) EXAM SOLVED PAPER PDF FREE DOWNLOAD
- BIHAR PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION ASSISTANT ENGINEER (BPSC AE) 2022 CIVIL ENGINEERING EXAM SOLVED PAPER WITH EXPLANATIONS PDF
- NHPC (NATIONAL HYDROELECTIC POWER CORPORATION) JUNIOR ENGINEER NHPC JE 2022 CIVIL ENGINEERING EXAM SOLVED PAPER PDF FREE DOWNLOAD

Leave a Reply