

CONTENTS
- THE PERMANENT WAY
- CAPACITY OF RAILWAY TRACK
- GAUGES IN RAILWAY TRACK
- SELECTION OF GAUGE
- UNIFORMITY OF GAUGES
- RAILWAY TRACK CROSS-SECTIONS
- CONING OF WHEELS
- TRACK STRUCTURE FOR B.G AND M.G ROUTES
- GRADIENTS AND GRADE COMPENSATION
- SPEED OF TRAIN
- RADIUS OF DEGREE OF THE CURVE
- SUPERELEVATION OR CANT
- STATIONS AND YARDS
- CLASSIFICATION OF RAILWAY STATIONS
- PLATFORMS
- MAINTENANCE OF TRACK
- BRIDGE ENGINEERING
- CLASSIFICATION OF BRIDGES
- COMPONENT PARTS OF A BRIDGE
- REINFORCED CEMENT CONCRETE BRIDGES
- CAUSEWAYS
- CLASSIFICATION OF CAUSEWAYS
- BRIDGE TERMINOLOGIES
- INSPECTION AND DATA COLLECTION
- TUNNEL ENGINEERING
- SHAPE OF TUNNELS
- SIZE OF TUNNEL
- TUNNELLING METHODS
- CONSTRUCTION EQUIPMENTS
- TUNNEL LINING
- VENTILATION OF TUNNEL

THE PERMANENT WAY
The combination of rails, fitted on sleepers and resting on ballast and subgrade is called permanent way. In a permanent way, the rails are joined in series by fit, plates and botts and then they are fixed to sleepers by different types of fastenings. The sleepers properly spaced, resting on ballast, are suitable packed with ballast. The layer of ballast rests on the prepared subgrade called the formation.
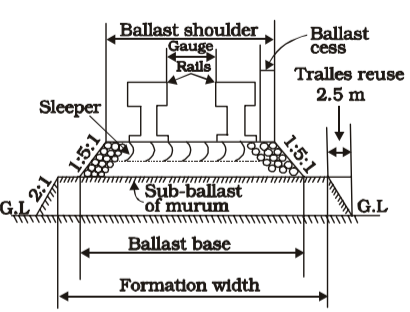
The rails acts as girders to transmit the wheel load to the sleepers. The sleepers holds the rails in proper position with respect to the proper tilt, gauge and level, and transmit the load from rails to the ballast. The ballast distributes the load over the formation and holds the sleepers in positions. On curved tracks, super-elevation is maintained by ballast and the formation is levelled. Minimum ballast cushion is maintained at the inner rail, while the rail gets kept more ballast cushion. Additional quantity of ballast is provided on the Quter cees of each track for which the base width of the ballast is kept more than for a straight track.

HIGHWAY ENGINEERING IES MASTER GATE STUDY MATERIAL : CLICK HERE
Requirements of an Ideal Permanent Way
Permanent track is regarded to be semi-elastic in nature. There is possibility of track getting disturbed by the moving wheel loads. The track should therefore be constructed and maintained keeping the requirements of a permanent way, in view so as to achieve higher speed and better riding qualities while less future maintenance. Following are the some of the basic requirements of a permanent way:
- The gauge should be correct and uniform
- The rails should be in proper level. In a straight track two rails must be at the same level on curves, the Quter rail should have proper super-elevation and there should be proper transition at the junction of a straight and a curve.
- The alignment should be correct i.e., it should be free from kniks or irregularities.
- The gradient should be uniform and as gentle as possible. Any change of gradent should be followed by a smooth vertical curve to give smooth riding quality.
- The track should be resilient and elastic in order to absorb shocks and vibrations of running track.
- The track should have enough lateral strength, so that alignment is maintained even due to effects of (a) side thrust on tangent lengths and centrifugal forces on curves (b) lateral forces due to expansion of rails particularly in case of welded rails.
- The radii and superelevation on curves should be properly designed and maintained.
- Drainage system may be perfect for enhancing saftey and durability of track.
- Joints, including points and crossing which are regarded to be weakest points of the railway track, should be properly designed and maintained.
- If there is trouble from the creep, the preventionary measures should be to prevent it.
- The various components of the track, i.e., the rails, fittings, sleepers, ballast and formation must fully satisfy the requirements for which they have been provided. If any component is lacking in fulfilling its requirements have been provided. If any component is lacking in fulfilling its requirements then either it should be improved or replaced.
- There should be adequate provision for easy renewals and replacements.
- The track structure should be strong, low in initial cost as well as maintenance cost.
TRANSPORTATION ENGINEERING ACE GATE STUDY MATERIAL : CLICK HERE
CAPACITY OF A RAILWAY TRACK
Capacity of a railway track (or track capacity) is hourly capacity of the track to hands the trains safely or in other words it is number of trains that can be run safely on a track per hour. The track capacity can be increased by the following ways.
- By achieving faster movement of trains on a track, and
- By decreasing the distance between successive trains.
The following are some of the general measurer which can be taken to increase the track capacity.
- All the trains should be made to run at the same speed for which uniformity of gauges and traction should first be achieved in the country.
- All sections should be made of equal lengths.
- Multi-aspect signalling should be adopted to alert the driver in advance of positions for various sections. For example, a multicolour light signal red, yellow, double yellow and green light colour will respectively give indication of danger (red), caution (Yellow), attention (double Yellow) and clear (green)
- The speed of train can be increased by adopting diesel or electric traction.
- The speed can also be increased by making suitable improvements in the existing tracks and removing the speed restriction if any.
- A reduction in the time of stoppages of trains.
- The length of sections should be decreased by providing additional crossing sections.
- The length of crossing sections (or looks) should be increased in order to enable the longer goods train to pass.
- New lines should be constructed for operational and industrial purpose.
- A quick arrangement for shunting to attach or detach the coaches i.e., additional operating facilities in the station yards should be provided.
TRANSPORTATION ENGINEERING MADE EASY GATE NOTES : CLICK HERE
UNIFORMITY OF GAUGES
Gauge to be used in a particular country should be uniform through out as far as possible, because it will avoid many difficulties experienced in a non-uniform system. The uniformity of gauges result in the following advantages:
- The delay, cost and hardship in trans hipping passengers are goods from the vehicles of one gauge to another is avoided.
- As the transhipping is not required, there is no breakage of goods.
- Difficulties in loading and unloading are avoided and labour expenses are saved.
- Possibility of theft and misplacement, while changing from one vehicle to another is eliminated.
- Large sheds to store goods are not required.
- Labour strikes, etc. do not effect the service and operation of trains.
- Surplus wagons of one gauge cannot be used to another gauge. This problem will not arise if gauge is uniform.
- Locomotive can be effectively used on all the tracks if a uniform type of gauge is adopted.
- Duplication of equipment such as platforms, sanitary arrangements, clocks etc is avoided. This saves a lot of extra expenditure.
- During military movement, no item is waste in changing persons and equipment from one vehicle to another if gauge is confirm
- It is quite expensive to convert one gauge into another at a later stage as it may require new rolling stock, fresh construction and widening of bridges and tunnels.
- Due to late arrival of trains at the junction, where change of gauge is involved, the missing links result in number of difficulties. Passengers have to pass time on platforms. In uniform gauge, this problem does not arise.
- (viii) Porter charges are increased when passengers have to change compartment due to a different gauge. This is avoided if gauge is uniform. In India, efforts are being made to convert all N.G. and M.G. lines to B.G. lines on important sections as and when funds are available.
NOTE: A SEPARATE STUDY MATERIAL FOR HIGHWAY ENGINEERING WILL BE POSTED SOON
TRANSPORTATION ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIAL FOR RRB JE PDF CIVILENGGFORALL
DOWNLOAD LINK : CLICK HERE
PASSWORD : CivilEnggForAll
OTHER USEFUL BOOKS
- BUILDING MATERIALS – MOCK TEST 1 (QUICK)
- TELANGANA STATE PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION – ASSISTANT ENGINEER 2023 – TSPSC AE 2023 CIVIL ENGINEERING EXAM SOLVED PAPER WITH EXPLANATIONS PDF FREE DOWNLOAD
- SSC JE 2023 CIVIL ENGINEERING (CPWD/CWC/MES) EXAM SOLVED PAPER PDF FREE DOWNLOAD
- BIHAR PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION ASSISTANT ENGINEER (BPSC AE) 2022 CIVIL ENGINEERING EXAM SOLVED PAPER WITH EXPLANATIONS PDF
- NHPC (NATIONAL HYDROELECTIC POWER CORPORATION) JUNIOR ENGINEER NHPC JE 2022 CIVIL ENGINEERING EXAM SOLVED PAPER PDF FREE DOWNLOAD

Leave a Reply