

CONTENTS
- CLASSIFICATION OF ROADS
- ROAD PATTERNS
- PLANNING SURVEYS
- HIGHWAY PLANNING IN INDIA
- SURVEYS
- HIGHWAY CROSS-SECTION ELEMENTS
- SIGHT DISTANCE
- SUPERELEVATION
- HORIZONTAL TRANSITION CURVES
- HIGHWAY MATERIALS
- SUB-GRADE SOILS
- STONE AGGREGATES
- TESTS ON ROAD AGGREGATES
- BITUMINOUS MATERIALS
- TESTS ON BITUMEN
- CUTBACK BITUMEN
- HIGHWAY PAVEMENTS
- STRENGTH CHARACTERISTICS OF PAVEMENTS

CLASSIFICATION OF ROADS
- Based on weather.
- All-weather roads
- Fair-weather roads
- Based on the type of carriage way or road pavement.
- Paved roads
- Unpaved roads (e.g. earth roads and gravel roads)
- Based on the type of pavement surfacing provided.
- Surfaced roads
- Unsurfaced roads
- Based on method of construction.
- Traffic volume (vehicle):
- Heavy traffic road;
- Medium traffic road,
- Light traffic roads
- Load transported or tonnage:
- Class I or Class A (tonnes/day),
- Class II or Class B etc.
- Location and function.
- Traffic volume (vehicle):
HIGHWAY ENGINEERING IES MASTER GATE STUDY MATERIAL PDF: CLICK HERE
MODIFIED CLASSIFICATION OF ROAD SYSTEM (Given by Third Road Development Plan 1981-2001)
- Primary system.
- Expressway
- National Highway (NH)
- Secondary system.
- State Highway (SH)
- Major District Roads (MDR)
- Tertiary system or Rural roads.
- Other District Road (ODR)
- Village Road (VR)
ROAD PATTERNS
- Rectangular or block pattern: Adopted in the city roads of Chandigarh
- Radial or star and block pattern
- Radial or star and circular pattern: e.g. Connaught place
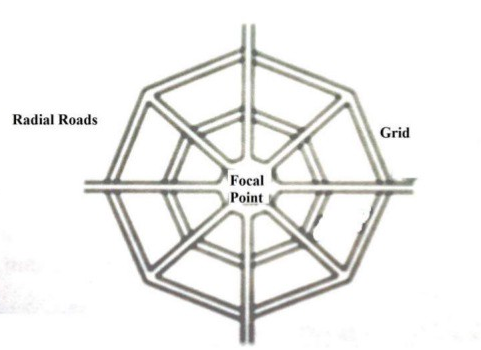
- Radial or star and grid pattern: Nagpur road plan formulae were prepared assuming star and grid pattern
- Hexagonal pattern
- Minimum travel pattern

TRANSPORTATION ENGINEERING ACE ACADEMY GATE STUDY MATERIAL PDF: CLICK HERE
SURVEYS
Engineering Surveys for Highway Location
Before a highway alignment is finalised in highway project, the engineering surveys are to be carried out. Survey stages. The survey may be completed in four stages.
1. Map study
2. Reconnaissance
3. Preliminary survey.
(a) Conventional approach by preliminary survey. It is carried out in following steps:
- Primary traverse
- Topographical features
- Levelling work
- Drainage studies and Hydrological data
- Soil survey
- Material survey
- Traffic survey
- Determination of final centre line.
(b) Modern rapid approach by aerial survey.
4. Final location and Detailed survey: The alignment finalised at the design office after the preliminary survey is to be first located on the field by establishing the centre line. Next detailed survey should be carried out for collecting the information necessary for the preparation of plans and construction details for the highway project. The data collected during the detailed survey should be elaborate and complete for preparing detailed plans, design and estimates of the project.
SIGHT DISTANCE
It is the length of road visible ahead to the driver at any instance. Three sight distance situations are considered in the design:
(1) Stopping Sight Distance (SSD) – The minimum sight distance available on a highway at any instant or spot should be of sufficient length to stop a vehicle travelling at design speed, safely without collision with any other obstruction.
(2) Over taking Sight Distances (OSD) – The minimum distance open to the vision of the driver of a vehicle intending to overtake slow vehicle ahead with safety against the traffic of opposite direction is called minimum overtaking sight distance (OSD) or safe passing sight distance.
(3) Sight Distance at Intersections – The IRC recommends that at uncontrolled intersections, sufficient visibility should be provided such that the sight distance on each road is atleast equal to the SSD corresponding to the design speed of the road. IRC recommends that a minimum visibility distance of 15 m along the minor road and a distance of 220, 180, 145 and 110 m along the major road corresponding to design speeds of 100, 80, 65 and 60 kmph. respectively may be provided.
TRANSPORTATION ENGINEERING ACE ACADEMY GATE NOTES PDF: CLICK HERE
SUPERELEVATION
In order to counteract the effect of centrifugal force and to reduce the tendency of vehicle to overturn or skid, outer edge of the pavement is raised with respect to the inner edge, thus providing a transverse slope throughout the length of horizontal curve. This transverse inclination to the pavement surface is called superelevation or cant or banking.
HORIZONTAL TRANSITION CURVE
Functions of the transition curves in the horizontal alignment of highway:
- To introduce gradually the centrifugal force between tangent point and the beginning of the circular curve, avoiding a sudden jerk on the vehicle.
- To enable the driver turn the steering gradually for his own comfort and security.
- To enable gradual introduction of the designed superelevation and extra widening of pavement at the start of the circular curve.
- To improve aesthetical appearance of the road.
SUB-GRADE SOIL
It is an integral part of the road pavement structure. The main function of the sub-grade is to give adequate support to the pavement and for this, the subgrade should possess sufficient stability under adverse climate and loading conditions.
STONE AGGREGATES
Aggregates form the major portion of pavement structure and they form the prime materials used in pavement construction.
Desirable properties of road aggregates.
- Capable of withstanding high stresses in addition to wear and tear.
- Aggregate should be hard enough to resist the wear due to abrasive action of traffic.
- Aggregate should be able to resist impact produced by heavily loaded steel tyred vehicles.
- The stone used in the pavement construction should be durable and should resist disintegration due to action of weather.
- Too flaky and too much elongated aggregate should be avoided as far as possible in road construction.
- The aggregates used in bituminous pavements should have less affinity with water when compared with bituminous materials.
TRANSPORTATION ENGINEERING MADE EASY GATE NOTES PDF: CLICK HERE
TEST FOR ROAD AGGREGATES
- Crushing test: The aggregate crushing value provides a relative measure of resistance to crushing under gradually applied compressive load.
- Abrasion test: Abrasion tests are carried out to test the hardness property of stones and to decide whether they are suitable for the different road construction works.
- Impact test: A test designed to evaluate the toughness of stone or resistance of the aggregates to fracture under repeated impacts is called impact test. The aggregate impact value indicates a relative measure of resistance of aggregate to impact, which has a different effect than the resistance to gradually increasing compressive stress.
- Soundness test: Soundness test is conducted to study the resistance of aggregates to weathering action.
- Shape test
- Flakiness index: It is the percentage by weight of aggregate particles whose least dimension/thickness is less than 0.6 of their mean dimension. This test is applicable for sizes larger than 6.3 mm
- Elongation index: It is the percentage by weight of particles whose greatest dimension or length is greater than 1.8 times their dimensions. This test is not applicable for size smaller than 6.33mm.
- Specific gravity and Water absorption test: The specific gravity of rocks vary from 2.6 to 2.9. Rock specimens having more than 0.66% water absorption are considered unsatisfactory unless found acceptable based on strength tests.
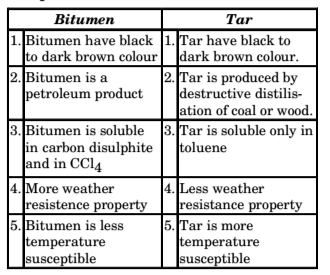
- Bitumen adhesion test: Adhesion problem of bitumen with aggregate are observed due to the pressure of water. Water liking aggregates are called hydrophiopic aggregate and they have greater alteration of bitumen than water.
TRANSPORTATION ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIAL FOR SSC JE PDF CIVILENGGFORALL
DOWNLOAD LINK : CLICK HERE
PASSWORD : CivilEnggForAll
OTHER USEFUL BOOKS
- BUILDING MATERIALS – MOCK TEST 1 (QUICK)
- TELANGANA STATE PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION – ASSISTANT ENGINEER 2023 – TSPSC AE 2023 CIVIL ENGINEERING EXAM SOLVED PAPER WITH EXPLANATIONS PDF FREE DOWNLOAD
- SSC JE 2023 CIVIL ENGINEERING (CPWD/CWC/MES) EXAM SOLVED PAPER PDF FREE DOWNLOAD
- BIHAR PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION ASSISTANT ENGINEER (BPSC AE) 2022 CIVIL ENGINEERING EXAM SOLVED PAPER WITH EXPLANATIONS PDF
- NHPC (NATIONAL HYDROELECTIC POWER CORPORATION) JUNIOR ENGINEER NHPC JE 2022 CIVIL ENGINEERING EXAM SOLVED PAPER PDF FREE DOWNLOAD

Leave a Reply